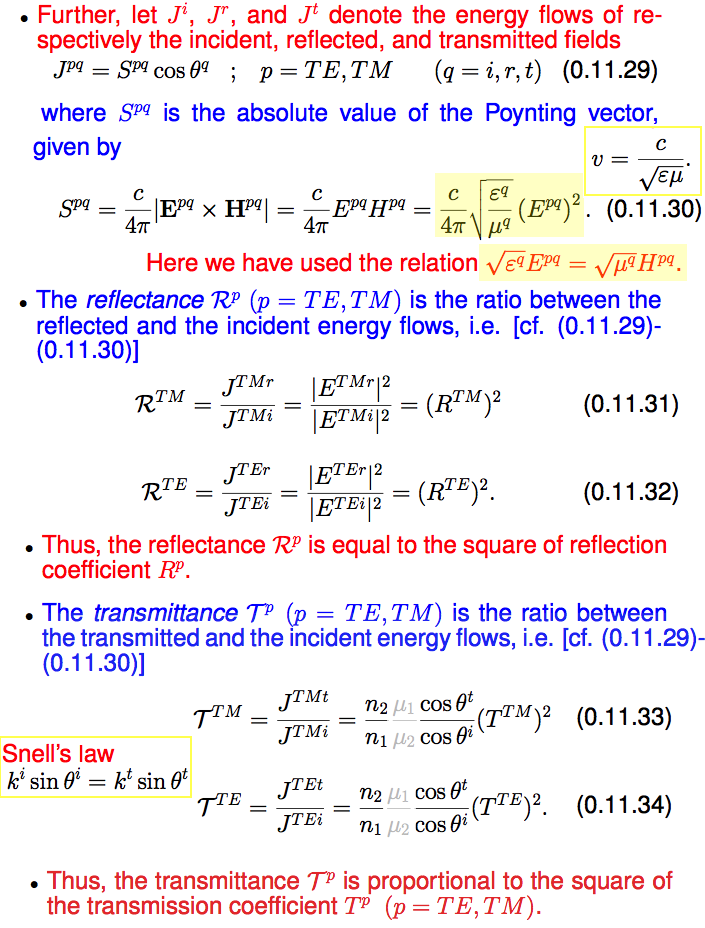
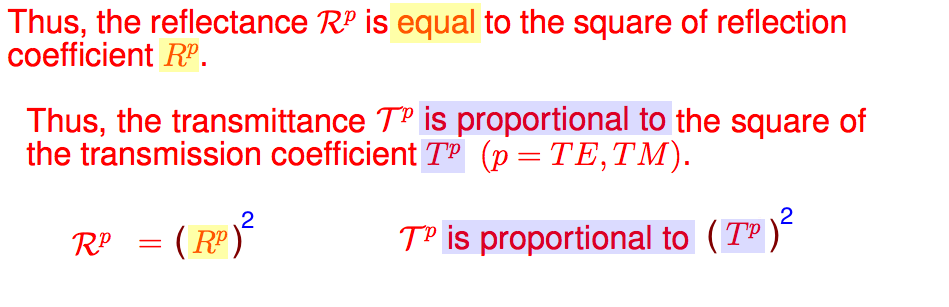
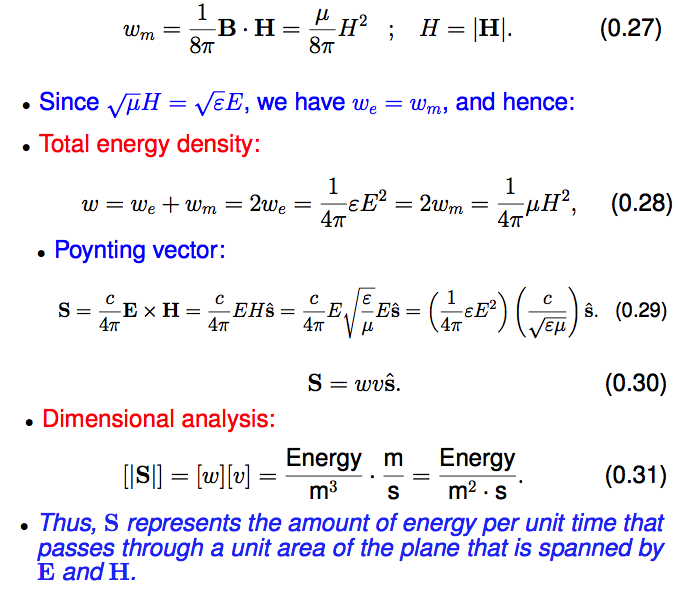
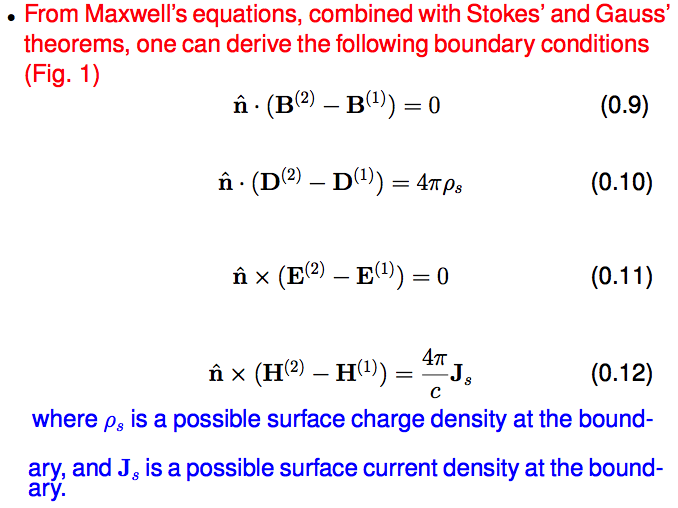
3a_S-polarized_R_and_T.png
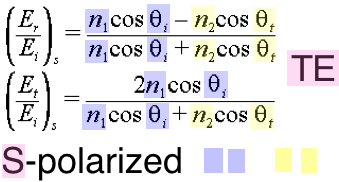
3a_S-polarized_R_and_T.png
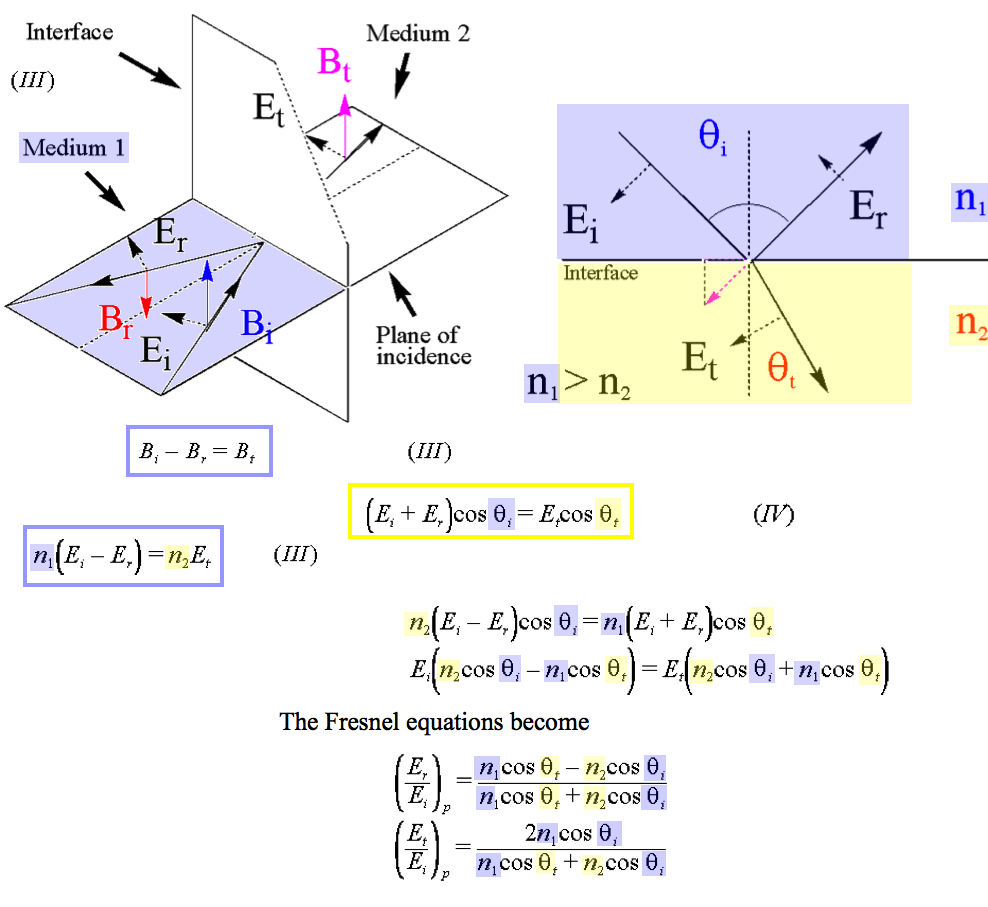
3b_P-polarized_R_and_T.png

3b_P-polarized_R_and_T.png
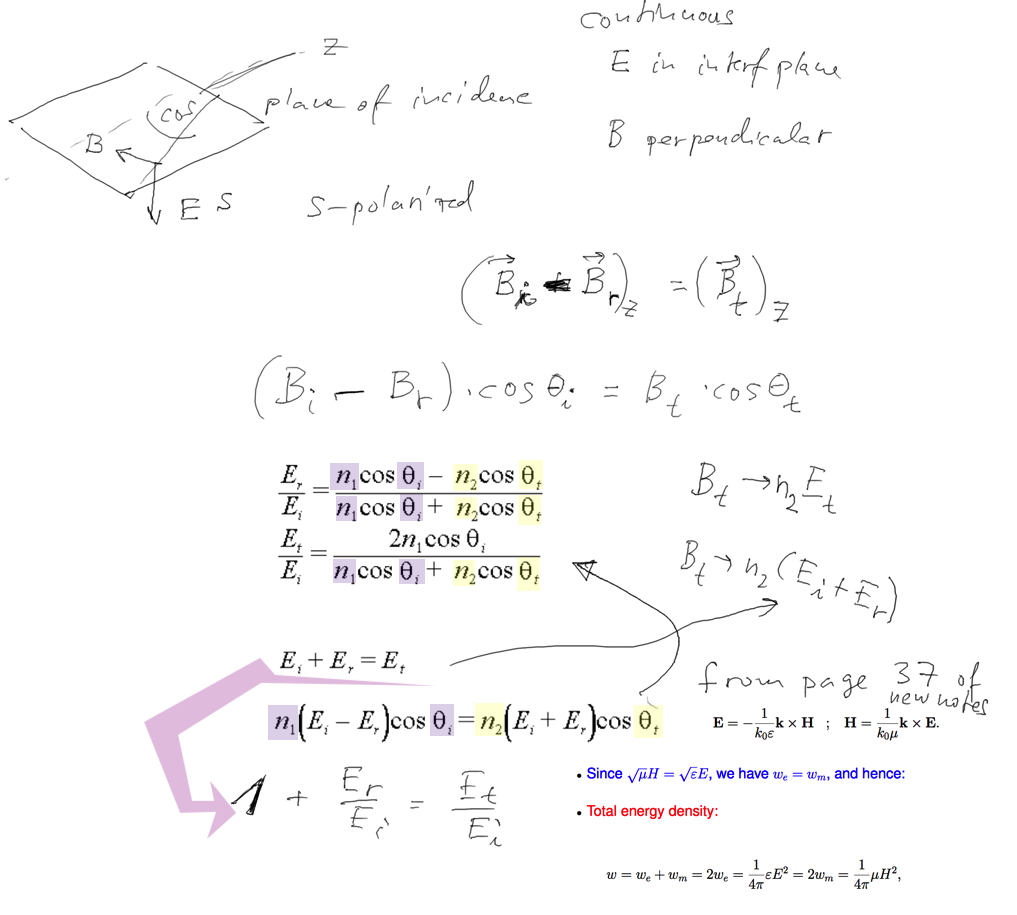
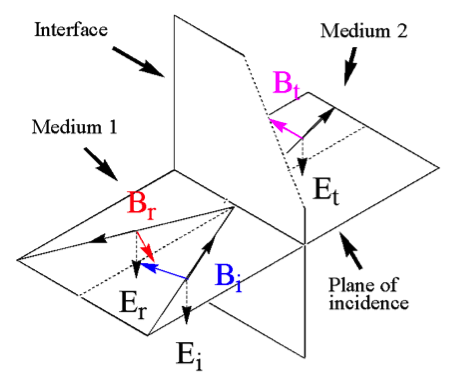
| S
TE 3a_S-polarized_R_and_T.png  3a_S-polarized_R_and_T.png |
P TM
3b_P-polarized_R_and_T.png  3b_P-polarized_R_and_T.png |