Physical Optics - Part 1
Physical Optics - the part of optics connected with the electromagnetic wave nature of light
Geometrical Optics, Ray optics - studies of propagation which are not connected with wave nature
Examples - polarization, dispersive media, reflection and refraction - how much is reflected? Diffraction, Interference.
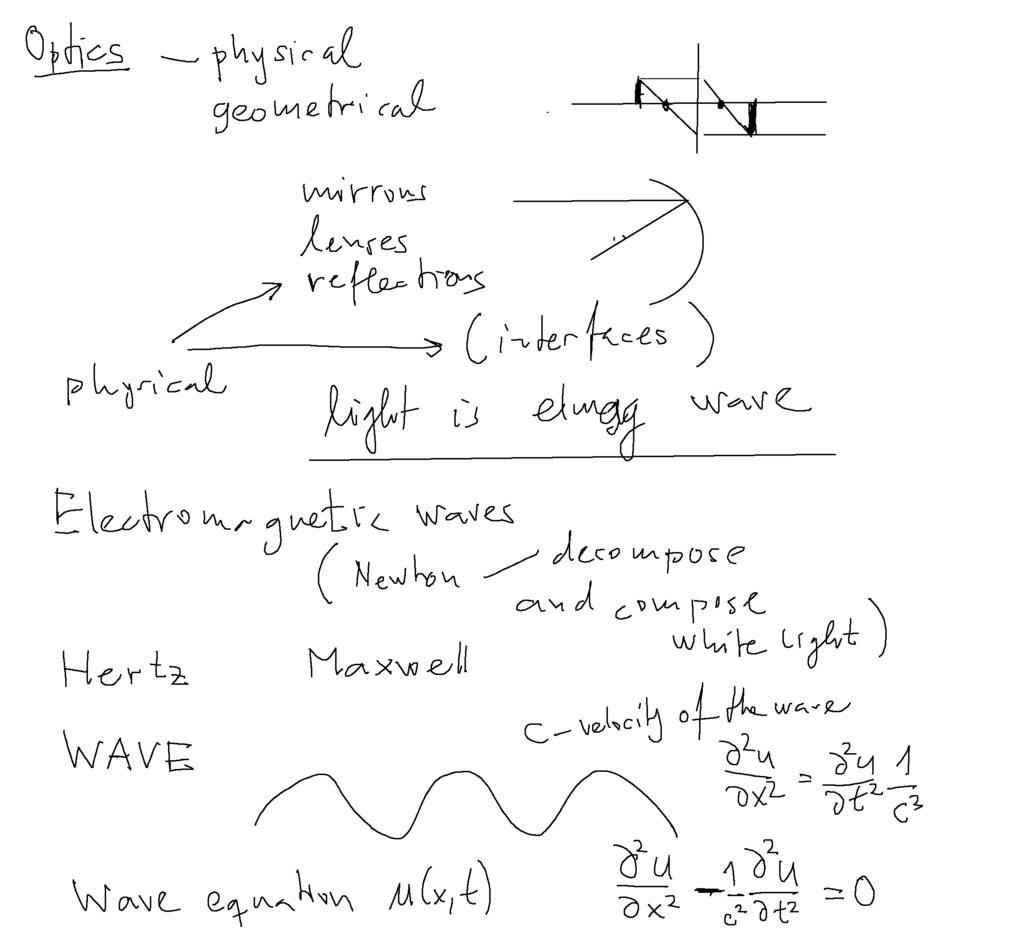
Wave equations - sound, water waves, mechanical waves
The nature of wave motion
1010_intro_electro_magnetic.png
Electricity and magnetism - thousands years of history - understanding and misunderstandings
Example - today's images under Magnetic Field
1012_magnetic_field_Google_Images.png
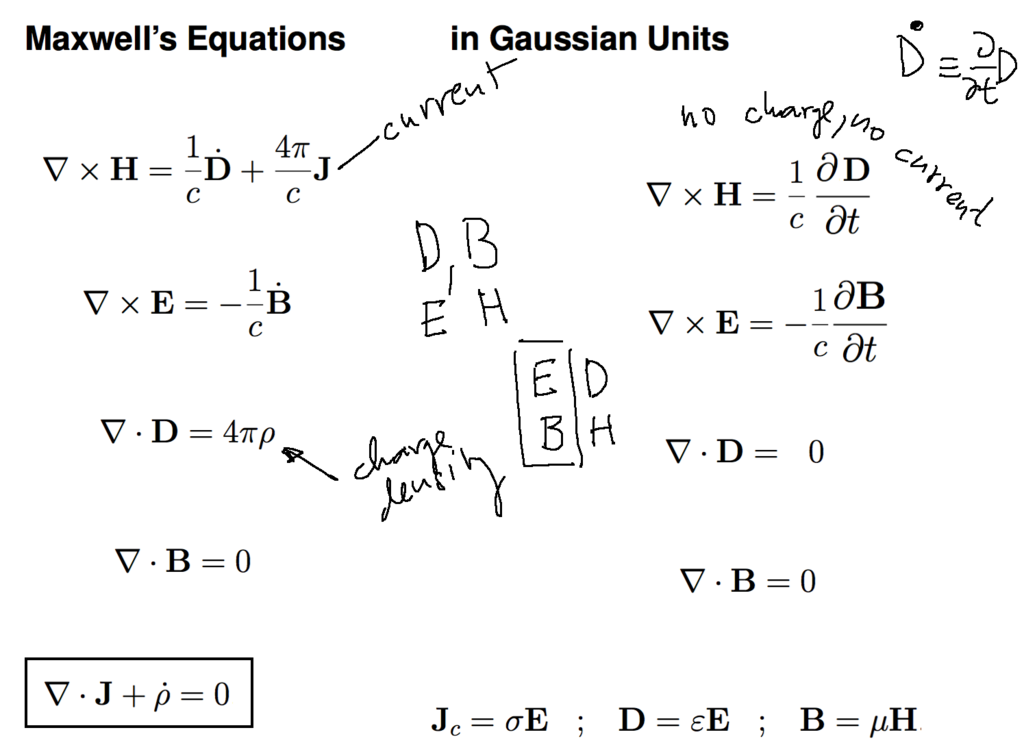
Maxwell's Equations - with speed of light c as a parameter - in so called Gaussian Units
In Gaussian set of thought in modern context - the B and H are "the same sort of quantity" - also E and D
- and all four have the same physical dimension ( in agreament with logical writing of special relativity )
1030_Maxwell.png
An important feature - "divergence free field" - the magnetic field strength.
A divergence - free field can always be written as a curl of a vector
In the same wave as a rotation-free field ( a field where the curl is zero, e.g. the static electric field )
can be written as a GRADIENT of a scalar field ( elecrostatic potential - a scalar )
The vector field generating the B is called - in analogy - a vector potential
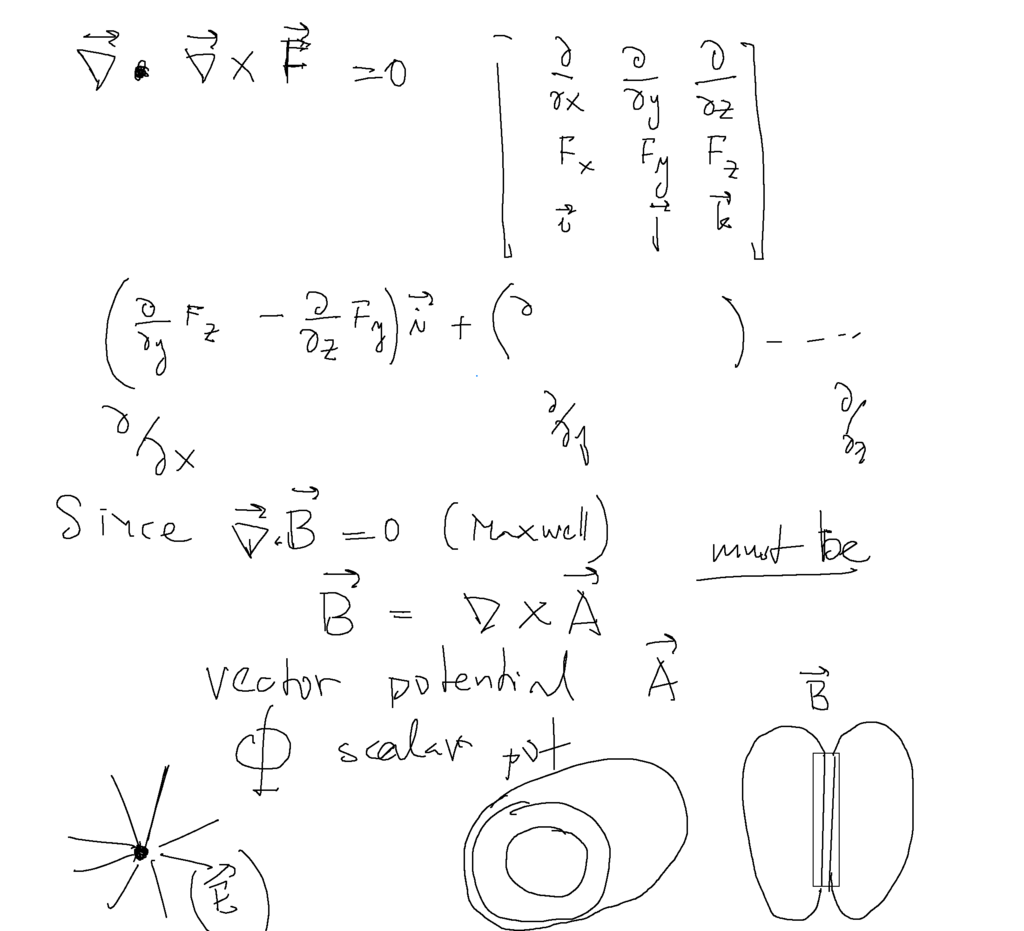
1020_divergence_free_div_B_0.png
To the right - Gaussian form of Maxwell equations in vacuum - B = H E = D
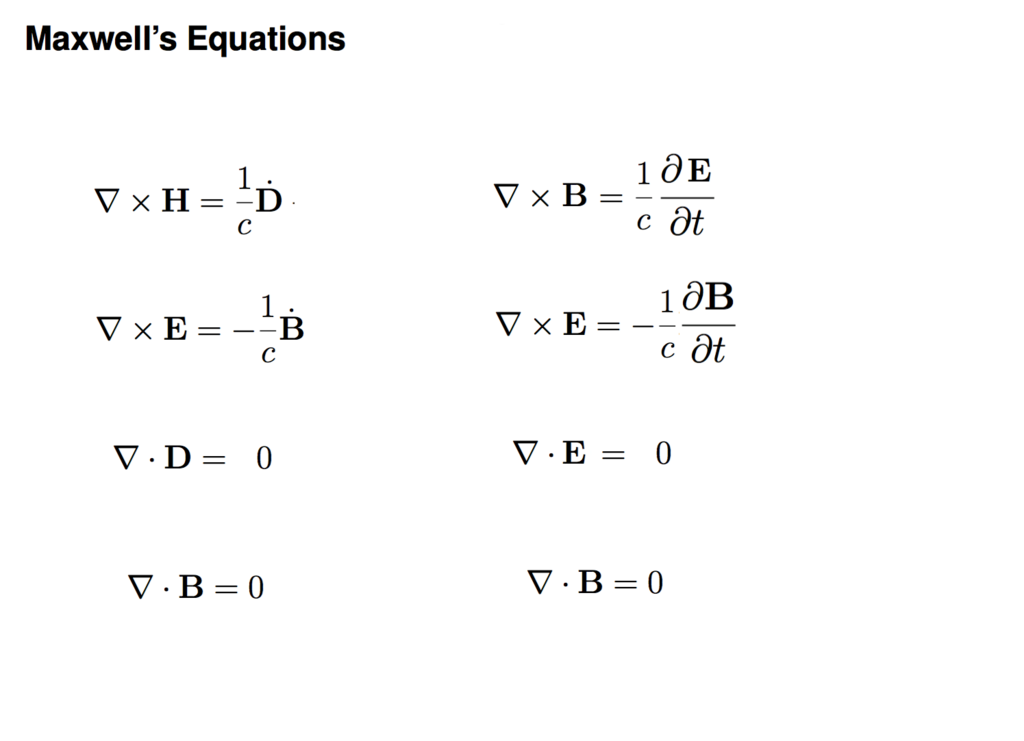
1035_Maxwell_Vacuum.png
There are 6 components of B and E ( 3 + 3 - vectors ).
But there are only 4 functions needed - 3 components of vector potential and 1 scalar potential - to specify the fields
And the physical fields are given by the derivatives of the four functions
Thus the four functions are not unique
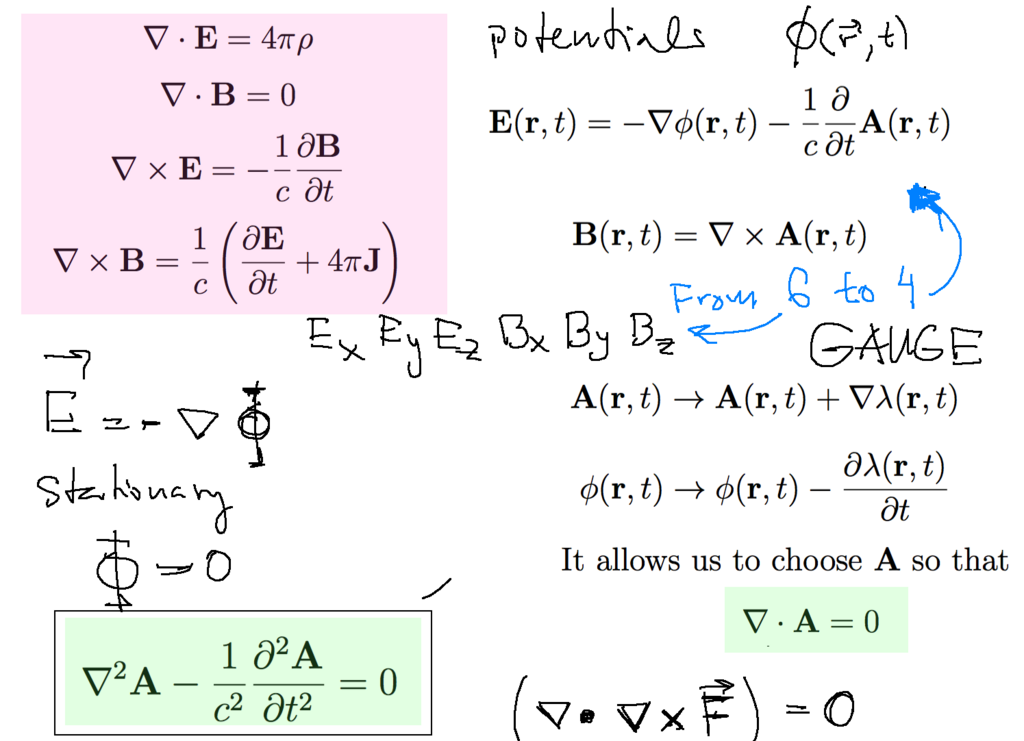
1040_VECTOR_POTENTIAL_GAUGES-.png
The analysis leads to the following picture of electromagnetic wave
In empty space Maxwell's equations give the following pattern of electric and magnetic field, propagating with velocity c
But there is also a circular polarization
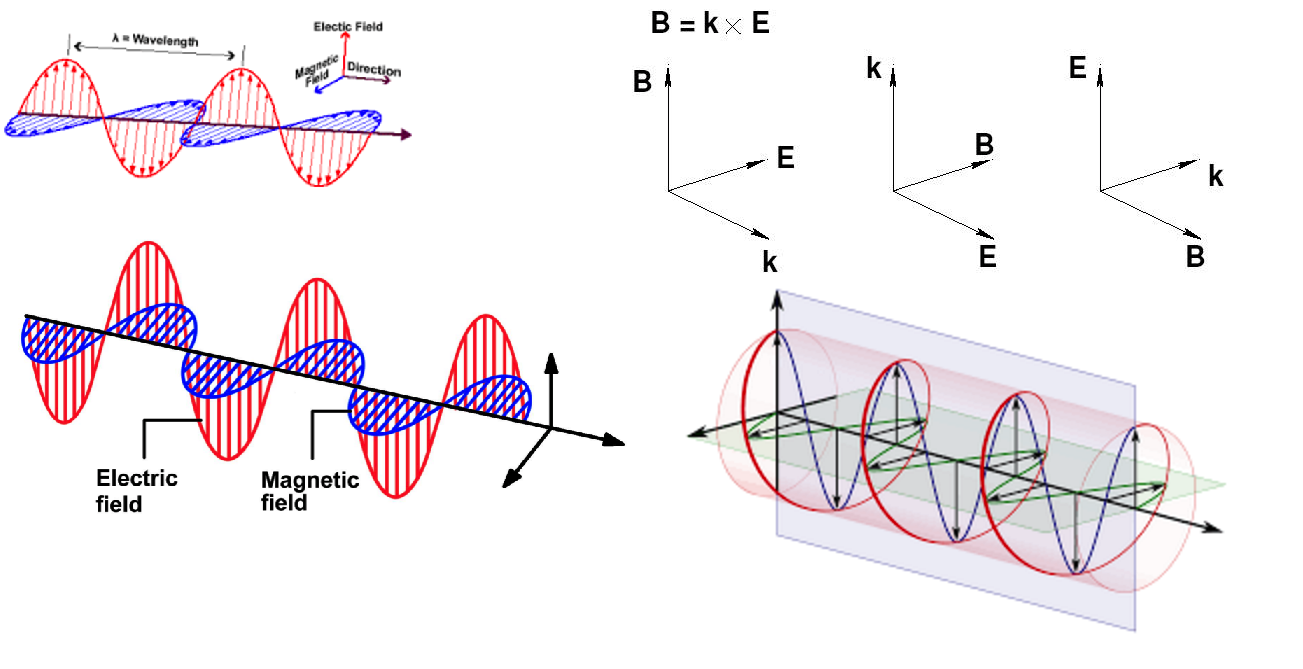
1045_Electromagnetic_Waves_geometry.png
Images for circular polarization - left and right polarization
1150_circular_polarized_Google_Images.png
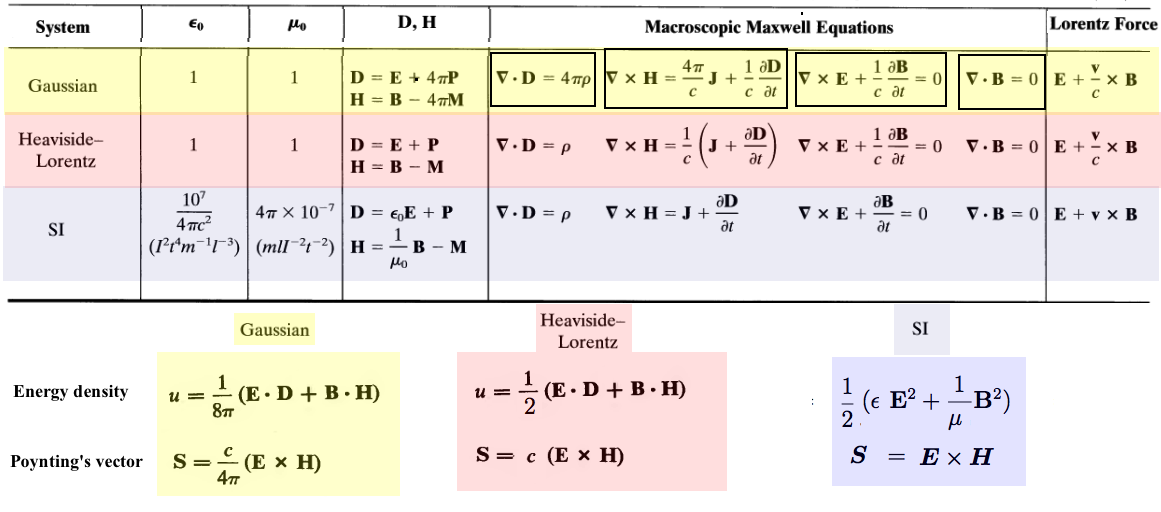
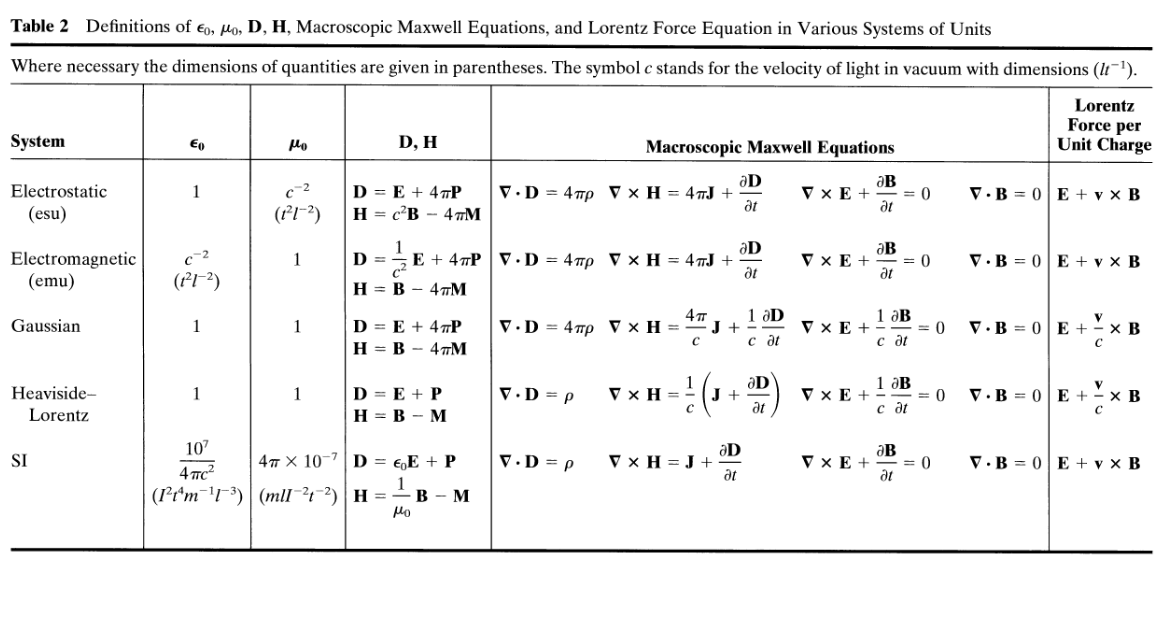
Maxwell's Equations - and the systems of units In addition to "permitivity of vacuum" and "permeability of vacuum" of SI
there is also the issue of factor 4 pi
This is connected with the Gauss theorem - basically it is the surface of unit sphere ( i.e. sphere of radius 1, or the full solid angle )
1200_Jackson_Table_colored.png
Jackson's Classical Electrodynamics has a very nice systematic presentation
1210_Jackson_table_2010.png
Maxwell's Equations in "Gaussian system" ( of units? - not - rather of physics thinking! )
We must return to the "systems of units"
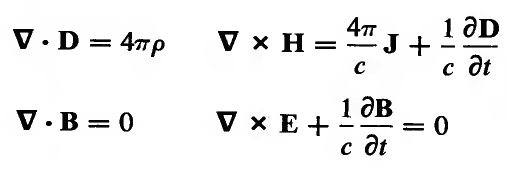
1300_Jackson_Maxwell_Gauss.png
Next time - why are Maxwell's equations an wave equation - see above
polarization
first apprach to "refraction"