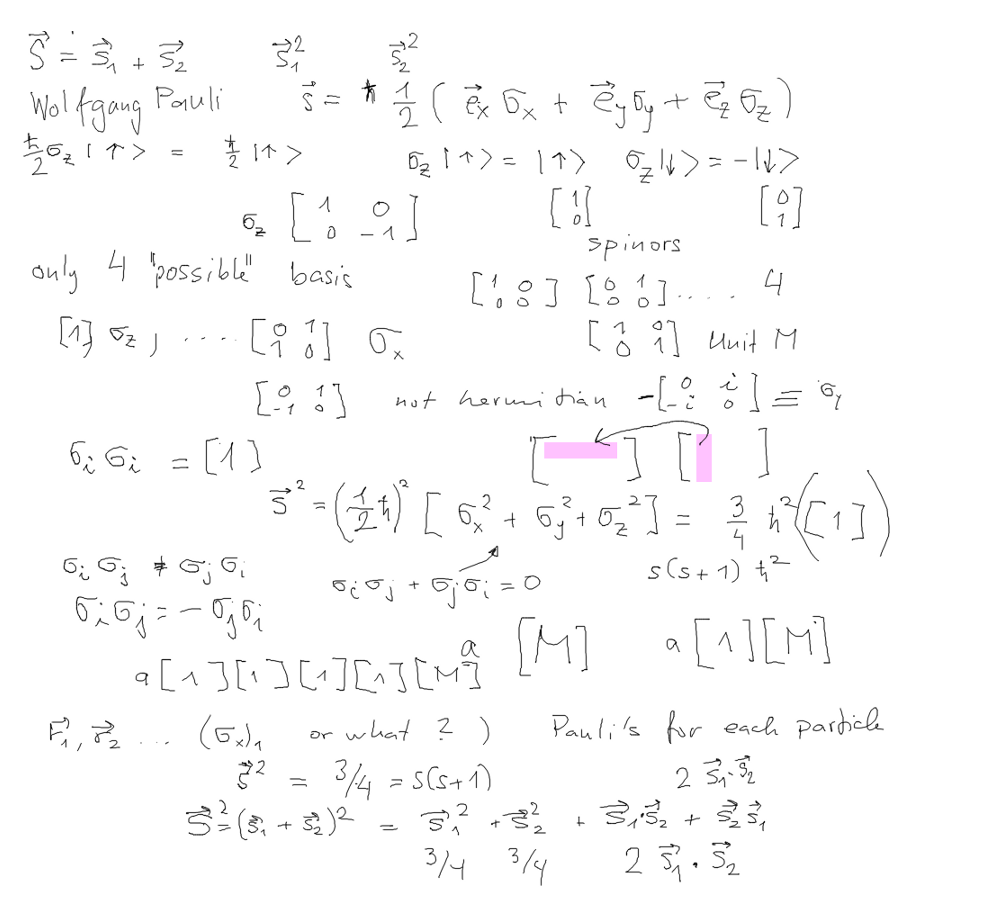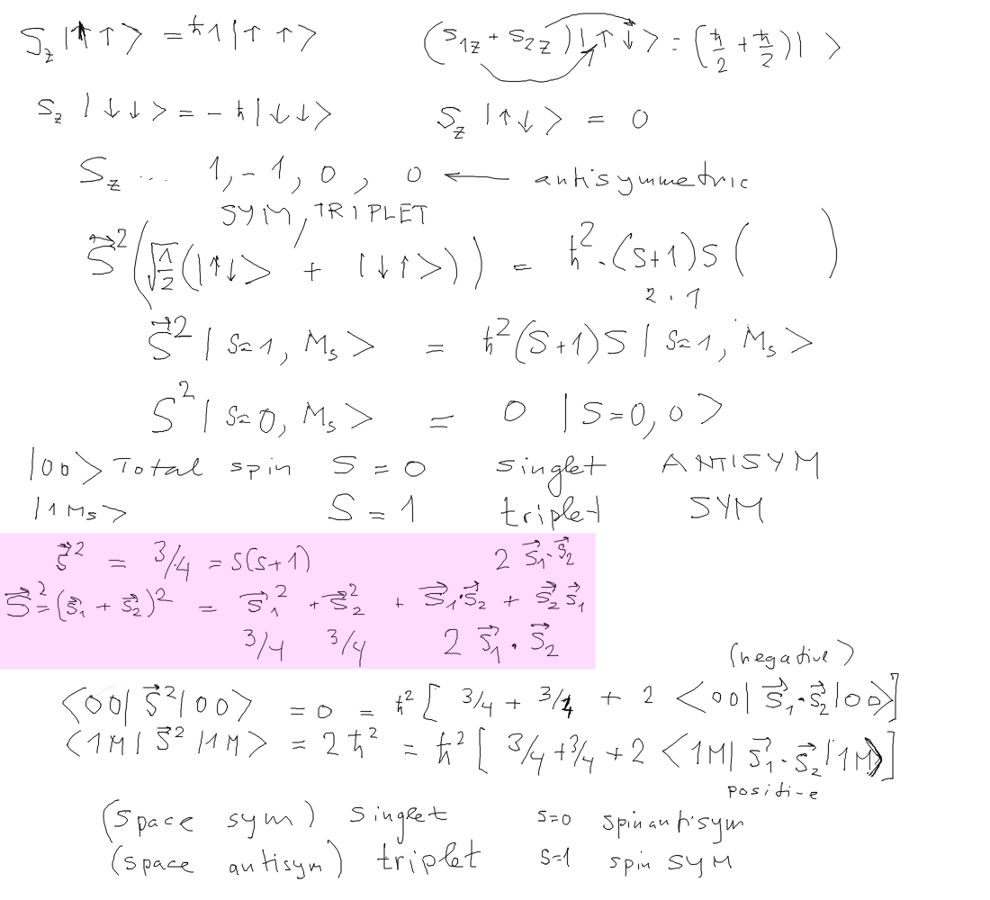SPIN - Two particles and spin;
Para- and Ortho- helium
Spin is basically more magnetic moment than angular momentum.
But angular momentum for charged particle
gives a magnetic moment (classically - the orbiting charged
particle makes a little current loop - and current loop
gives magnetic moment (if you do not remember, check the wikipedia)
Here we mentioned some properties of L and S. The spins have
half-integers, and the "real" spin is 1/2
(but the spin magnetic moment has one unit (1 Bohr magneton, not 1/2
- we shall discuss this later in the course).
Projections on "z-axis", up and down (or left and right -
explanation - without
extra interaction - degenerate. Adding magnetic field - we get
additional energies - and one special
direction - the vector of the magnetic field strength.
In our context here we do not "see" spin, except due to the
Pauli principle / symmetries of wavefunctions
1_two_spins-only-free-otherwise.png
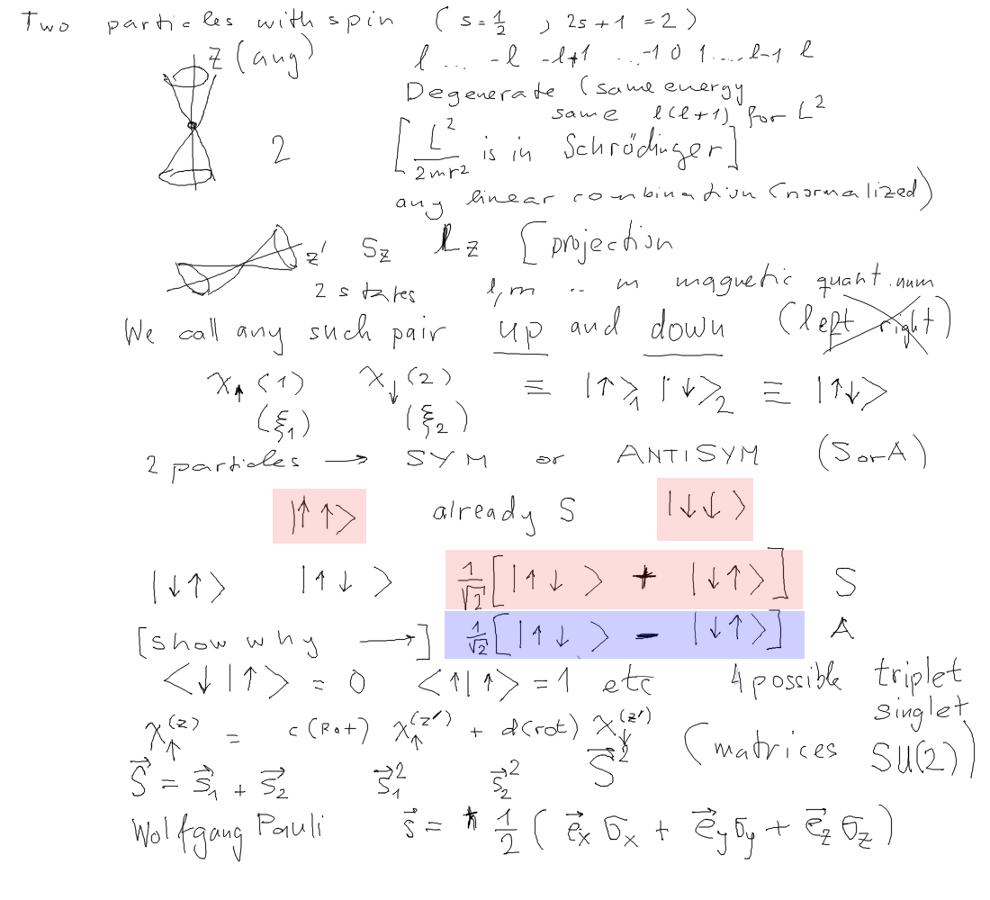
1_two_spins-only-free-otherwise.png
Pauli matrices are the realization of the spin operations
We mention Pauli matrices, matrix operations, Linear Algebra
basics
2_spin_Pauli_matrices.png
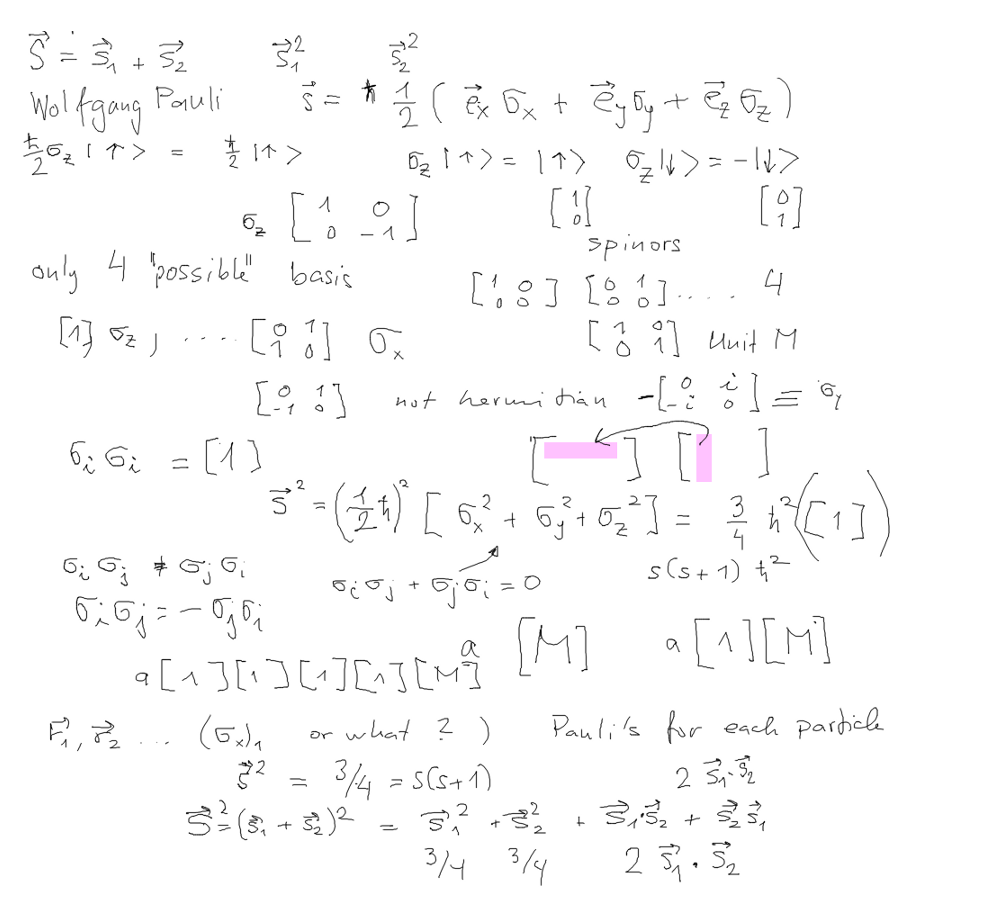
2_spin_Pauli_matrices.png
Why do we often just write 1 instead of unity matrix - because as
operation it is the same - leave unchanged
PROVIDED that all the operations are on the same BASIS
one spin - two states; two spins - two times two = 4 states
(note TIMES, not AND)
and they fall into 1 triplet (3) and one singlet (1)
3_two-spin-S_s1_s2_S_z_SYM_ASYM.png
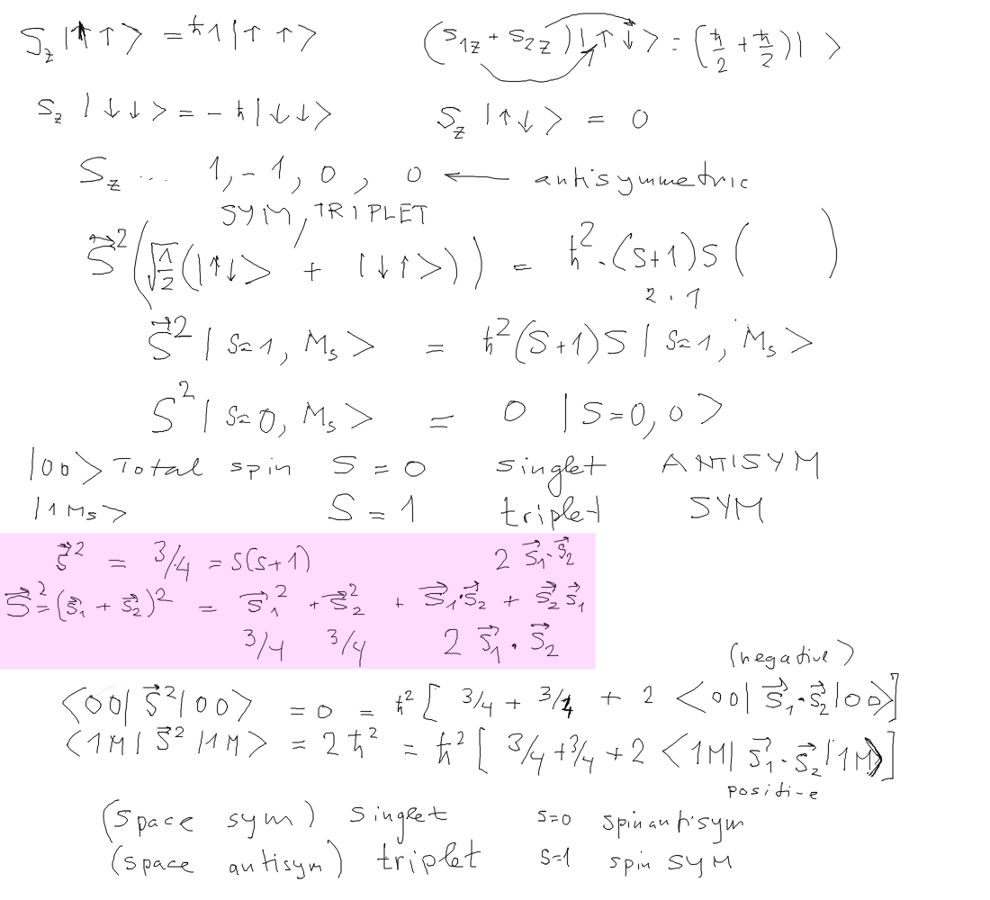
3_two-spin-S_s1_s2_S_z_SYM_ASYM.png
Square of L, square of S - eigenfunctions (addition of angular
momenta -
we have forgotten to mention TRIANGLE
RELATION L1 + L2 ->
L | L1 - L2 | <=
L <= L1 + L2
and that is valid for all operations following the angular momentum
rules
Here is the main physical result of our discussion:
The triplets get reduced repulsion between electrons; therefore the
triplets
have LOWER ENERGY compared to the the SINGLET of the same orbitals.
4_Triplet_lower_energy_as_REPULSION_REDUCED_spaced_ANTISYM.png

4_Triplet_lower_energy_as_REPULSION_REDUCED_spaced_ANTISYM.png
This lowering of triplet (symmetric spin) arrangements appears
as spin-spin attraction,
it appears that the (magnetic dipoles) of the electrons interact
with the strength comparable
to the electic interactions (the magnetic moments magnetic
interaction happens to
be much weaker). This type of exchange interaction is general for
all electrons.
It thus happens to be the origin of FERROMAGNETIC BEHAVIOUR (e.g.
Heisenberg model
of ferromagnetism)
5_Exchange_interaction_effective_spin_spin.png

5_Exchange_interaction_effective_spin_spin.png
What else about helium: Better model wavefunctions - THE
VARIATIONAL METHOD(S)
For that we shall have a look how the reulsion is evaluated.
6_what_else_about_Helium.png
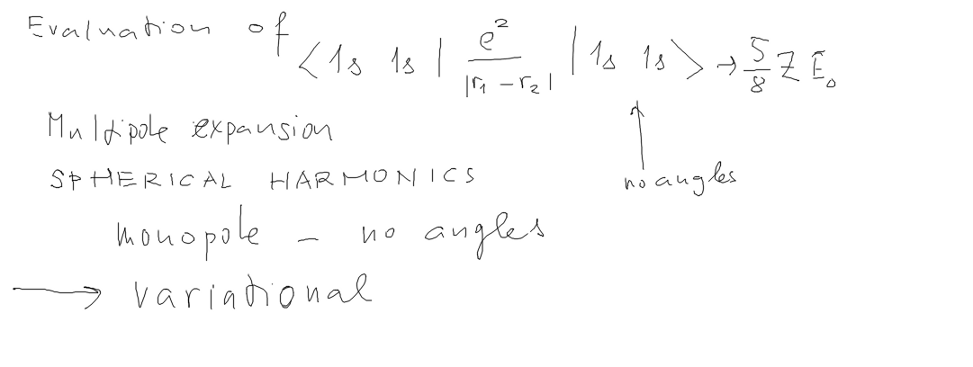
6_what_else_about_Helium.png
Finally, we shall also discuss the doubly excited states of
helium (autoionization)