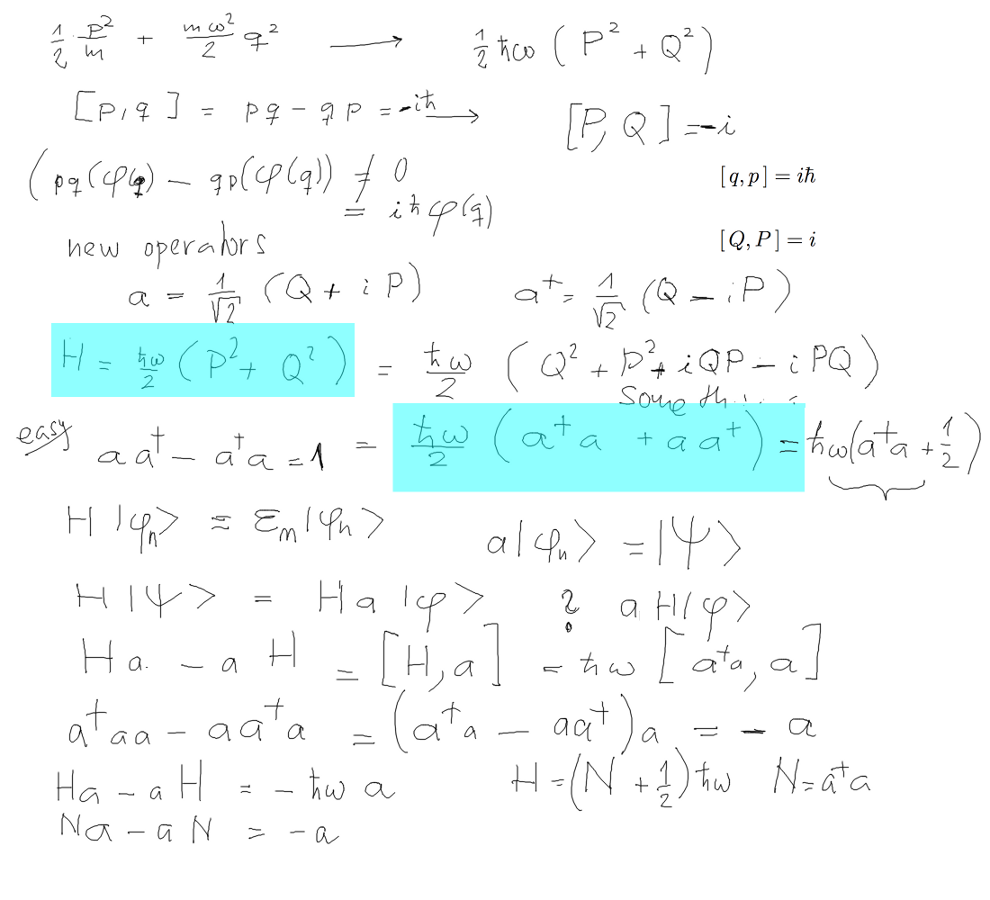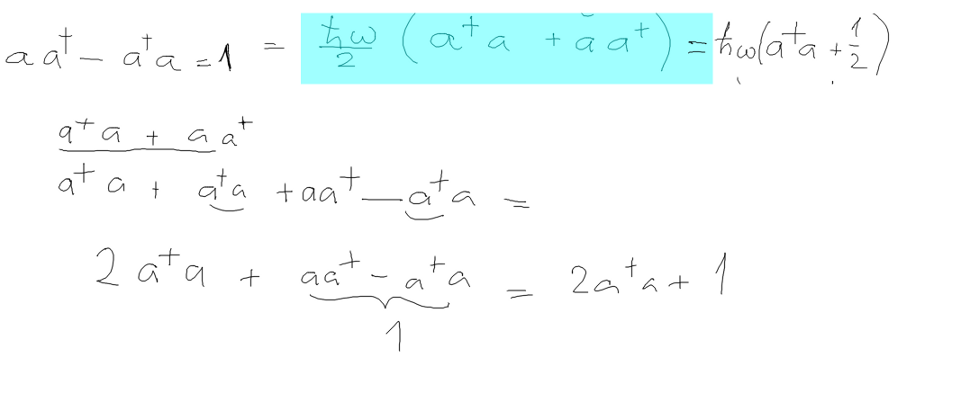System of oscillators is a model. For any system in equillibrium -
there is a minimum in potential energy,
i.e. no forces - forces would cause accelerarations and thus motion.
Minima in potential(s) - the expansions lead to V(xi, xj,...
xn) -> k ( xi, - xj )2
+ O( ( xi, - xj )3) + ....
Thus it mathematically looks as a system connected by springs, or
(coupled) harnonic oscillators.
We shall see that many other systems (like electromagnetic fields )
can be brought to a similar model,
through the concept of eigenmodes.
Eigenmodes for a coupled system of vibrations - classical energy
written in most general form.
1_systems_coupled_oscillators_eigenmodes.png

1_systems_coupled_oscillators_eigenmodes.png
Here above - how the string of balls connected by springs obeys this
form.
Eigenmodes sketched
2_systems_coupled_oscillators_eigenmodes.png

2_systems_coupled_oscillators_eigenmodes.png
Quantum mechanics of an harmoic oscillator in algebraic
formulation
Transform to dimension-less form - operator q (position) and p (momentum) to dimension-less
Q and P
3_Harmonic_Oscillator_Algebraic_Method.png
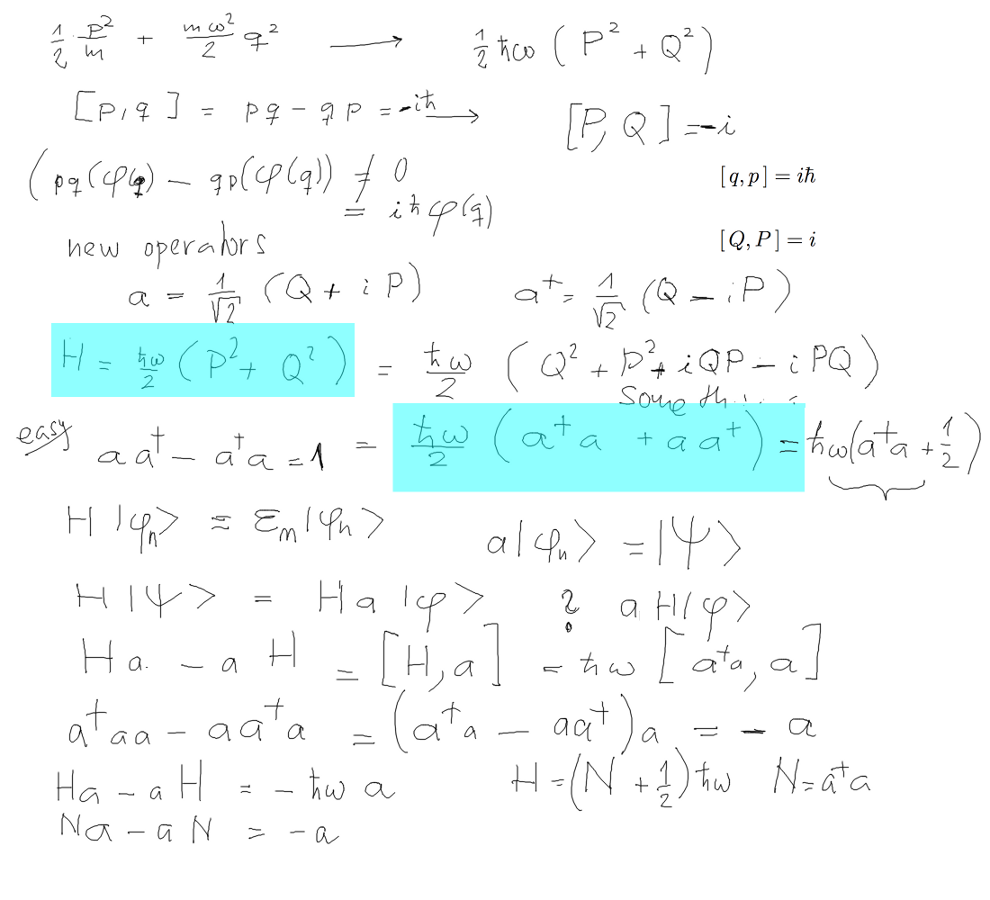
3_Harmonic_Oscillator_Algebraic_Method.png
We have defined a transformation Q, P -> a+
, a - called creation and annihilation operators -
see bellow
ALSO N = a+
a - will be called Number
operator
4_transforming
_a.plus_a.png
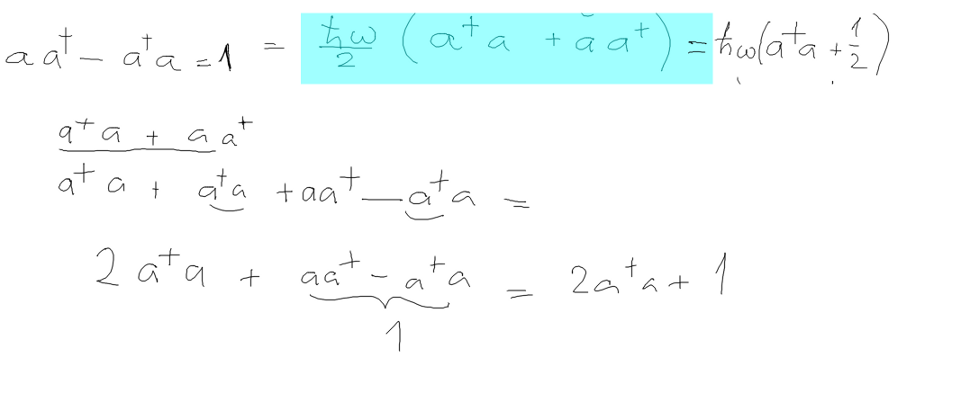
4_transforming
_a.plus_a.png
Here we work with N = a+
a - called Number
operator and we see why
Commutation of N = a+
a with a+
and a ( starting with a )
5_H_O_Algebraic_Method_1.order.diff.eq.png

5_H_O_Algebraic_Method_1.order.diff.eq.png