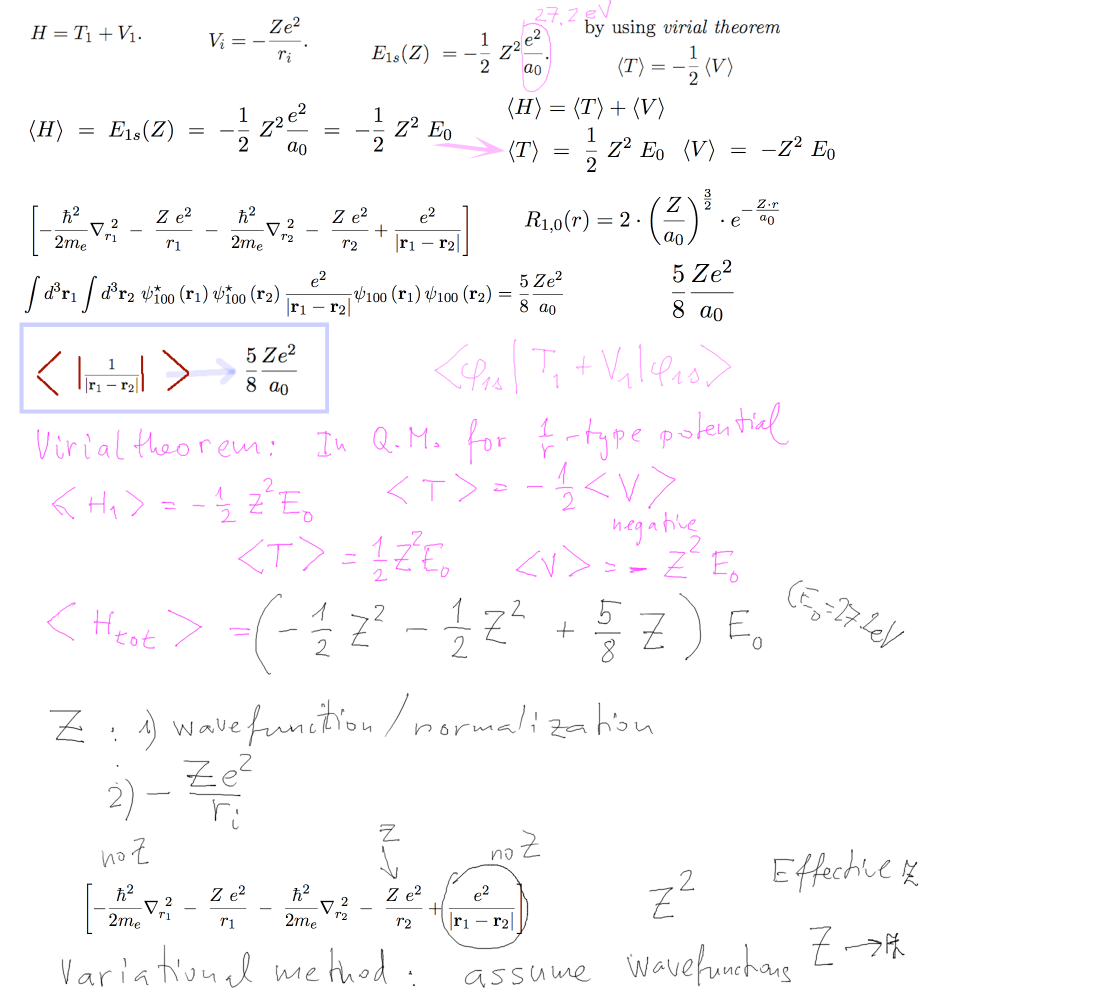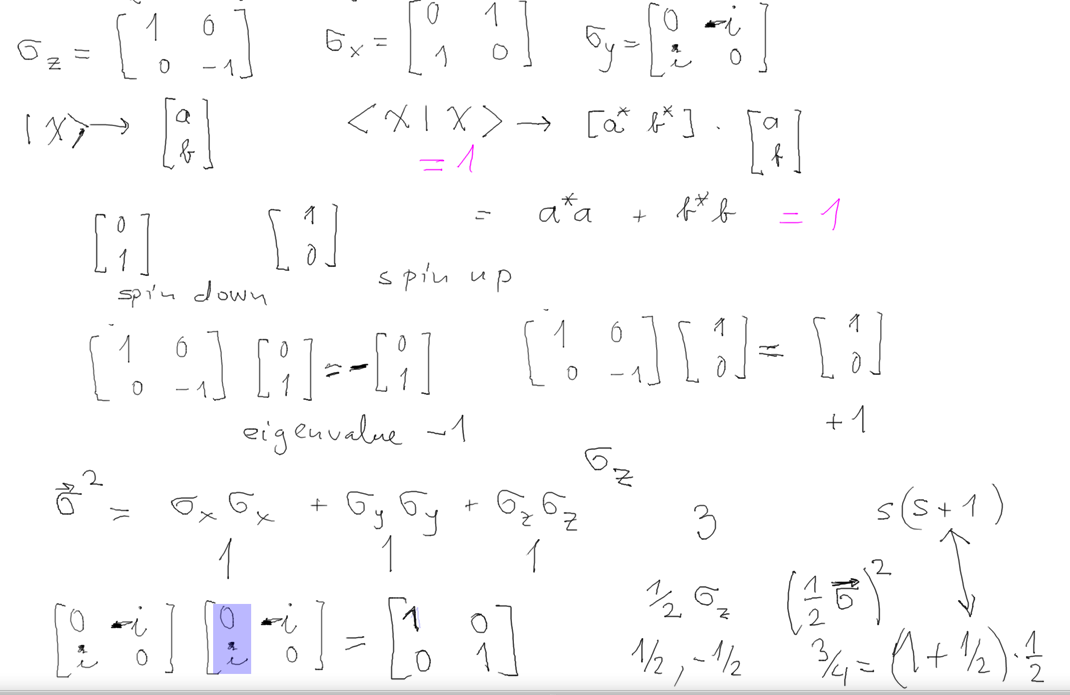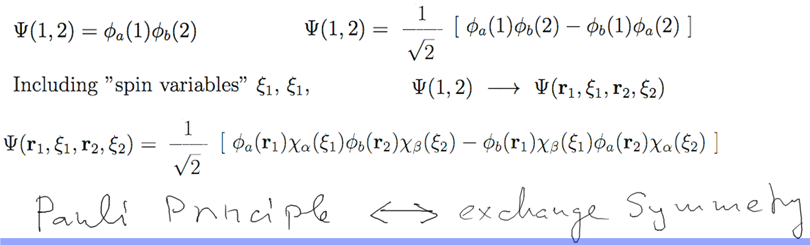Variational Method
Evaluting the independent electron model for variable Z - nuclear
charge
The contribution from T and from V - see virial theorem - general
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virial_theorem
and for our case - power of radial distance potential -
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virial_theorem#Special_case_of_power-law_forces
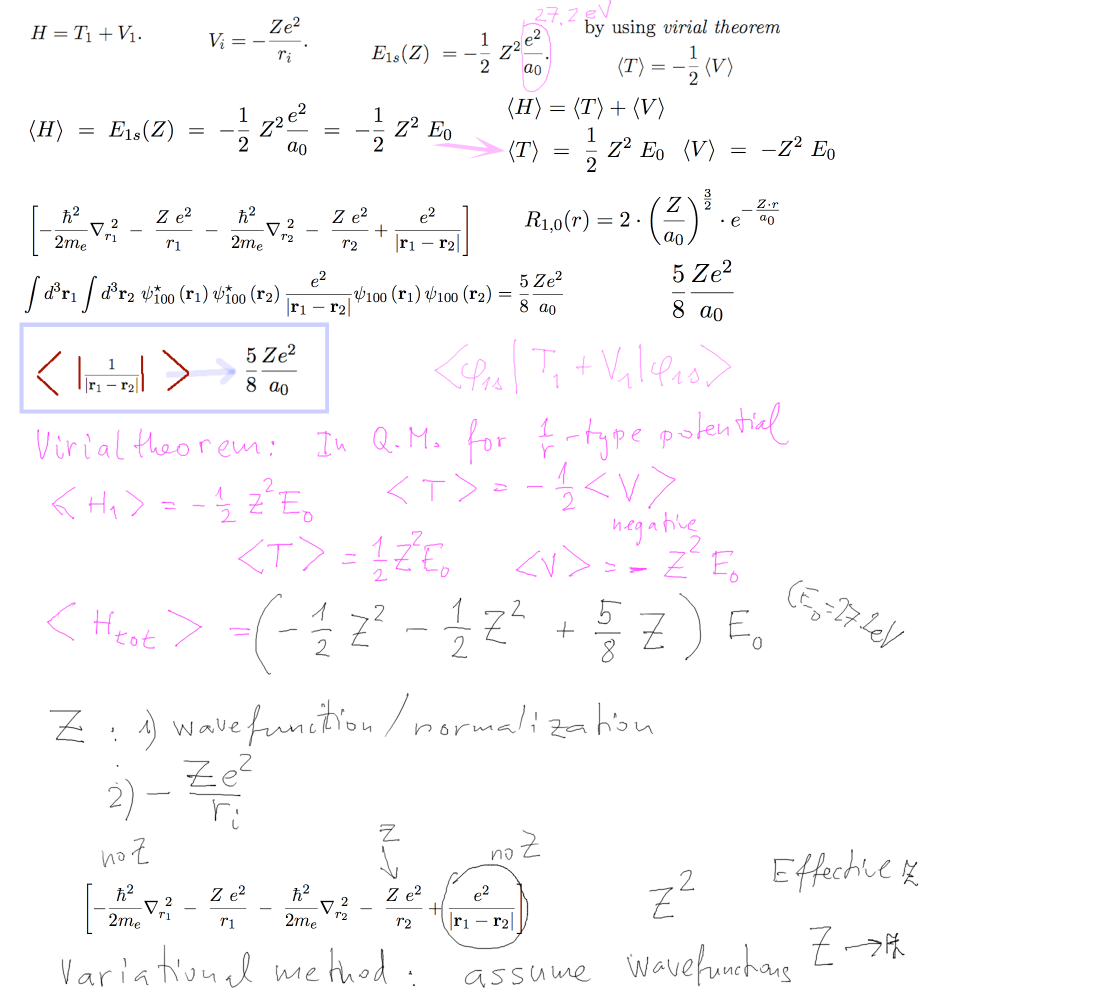
a1-variational-method.png
In the next slides we shal see why we should replace Z by an effective z which can be made variable - to
find the "best"
.... each of the 2 electrons "sees" the nucleus partially covered
by the other electron
Wavefunction depends on Z - that we make into z -
variable
Attraction to nucleus contains Z - that can not be variable
We shall find which power of Z or z

a2-variational-method-MINIMUM.png
Here we have seen that the <phi | H |
phi > can be made least possible - and that will
give best possible wavefunction
(At least from the point of view of the energy. some other quantities
might not be correctly represented)

a3-variational-method-result.png
And indeed, we have found above the solution.
ELECTRON SPIN

b1-Spin_angular_momentum_magnetic.png
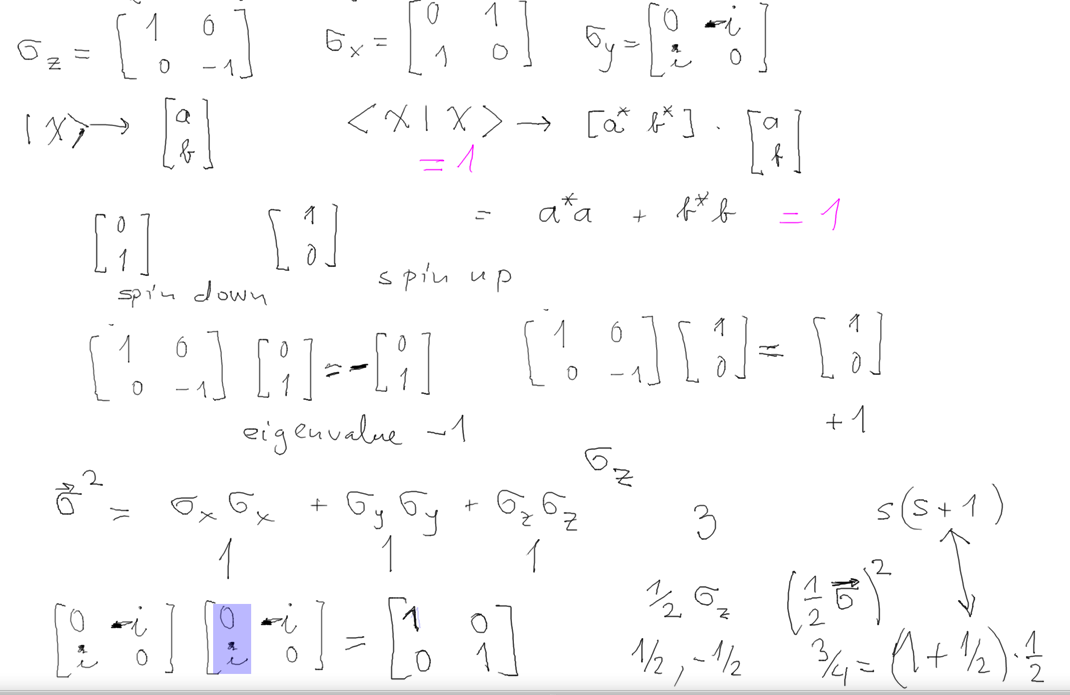
b2-spin-Pauli-Matrices.png
SPIN AND TWO ELECTRON
STATES - Continue next time
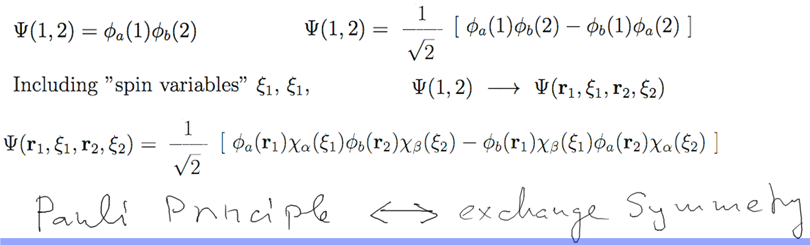
b3-spin-two-particles.png
Next time:
exchange symmetry
excited states
electron correlations - beyond independent electrons
configuration mixing
automatically generated by awk