In this lecture
1. Exponential decay from constant rate
2. Natural line width
3. Density of states - for light waes ( photons )
4. Eigenmodes of harmonic systems (coupled oscillations)
1. Exponential decay from constant rate we must modify the constant rate - depends also on "how much is left"

1000_Constant_RATE-decay.png
Exponential decay from constant rate and Natural line width part 1 - from the exponential decay result

1010_Exponential_Decay_Line_width.png
The assumption of perturbation theory can not be kept ( c0 = 1 must be replaced by square root of probability - look above )
Exponential decay from constant rate -----> Natural line width
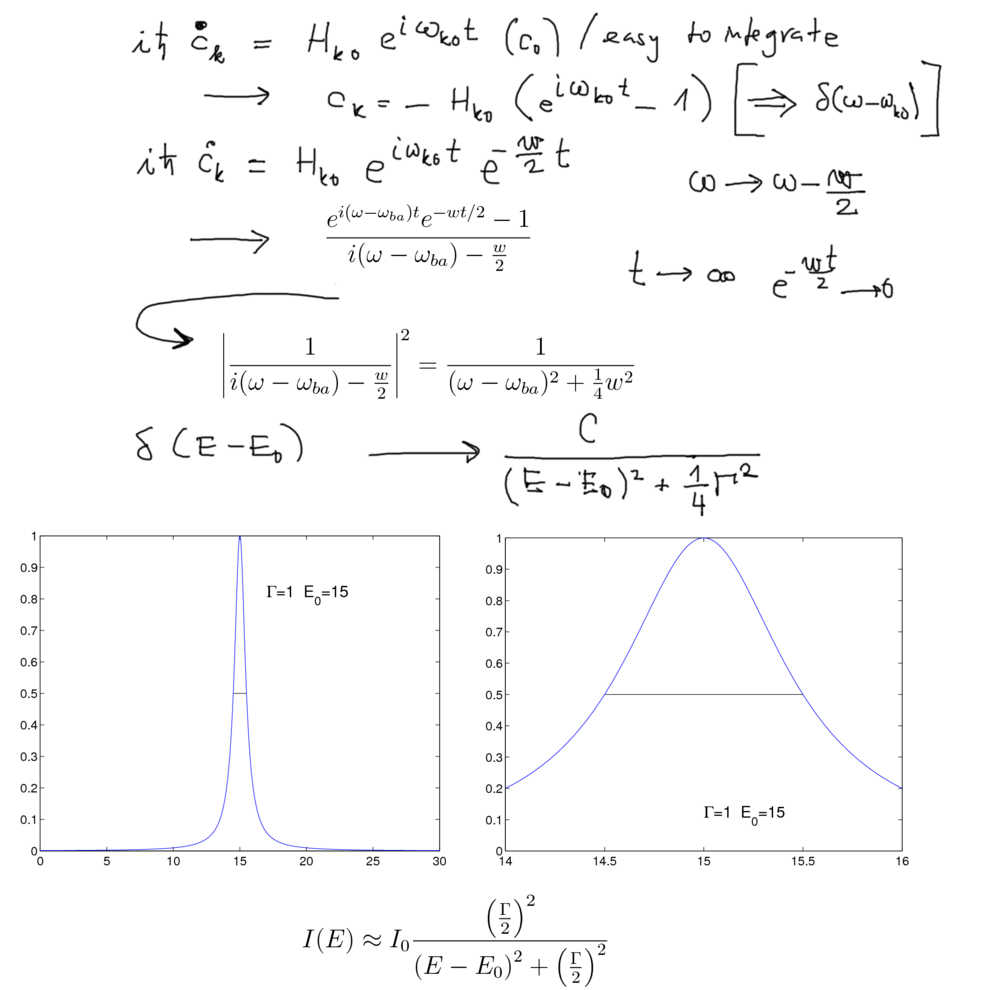
1020_Line_Width_replaces_Dirac_Delta.png
as opposed to random background phenomena - Gaussian shape ( G(E, E0) =) exp(- (E - E0)^2 / Delta^2 )
Natural line width (Lorentz shape)
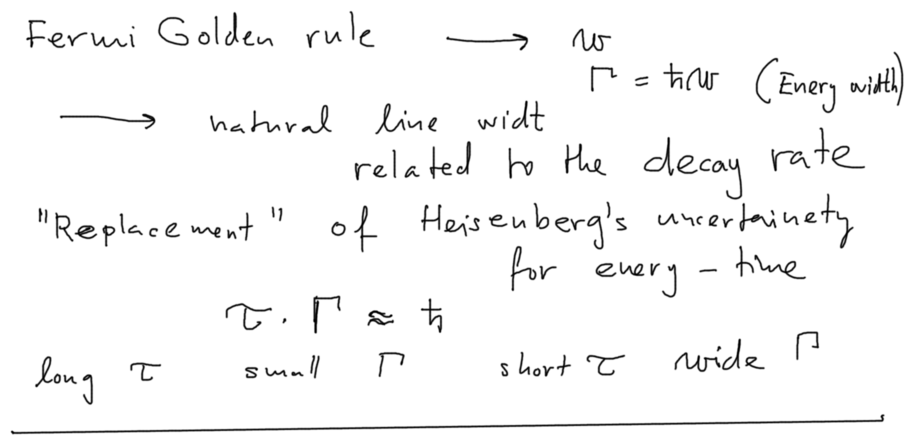
1030-Summary-Line_Width_NO_Dirac.png
Density of states - for light waves ( photons ) - Discretization by periodic boundary conditions
The density of states appears whenever we replace a summation by an integral
This is always so: summation ---> integral allways needs "density of states"
(also in the Golden Rule derivation last time)
Dimensional argument
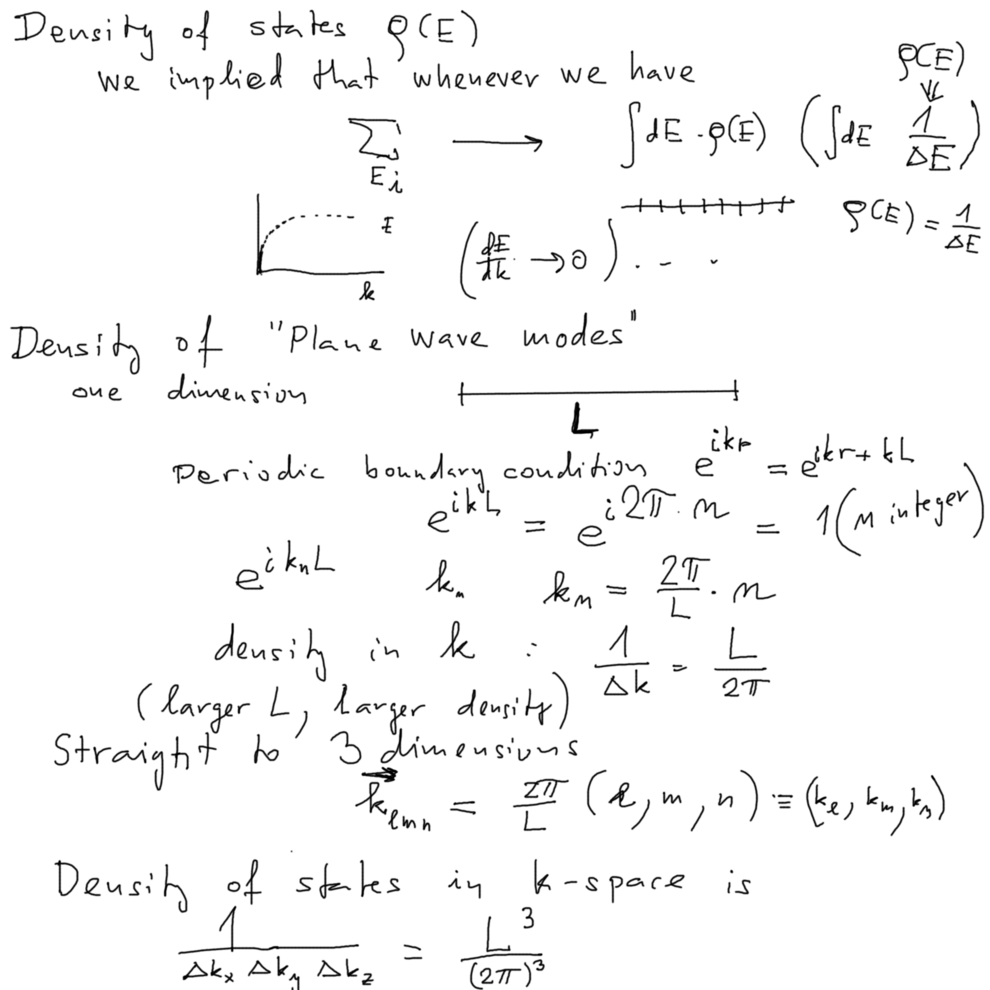
1100_Density_of_states.png
Density of states - for light waes ( photons ) Discretization by periodic boundary conditions
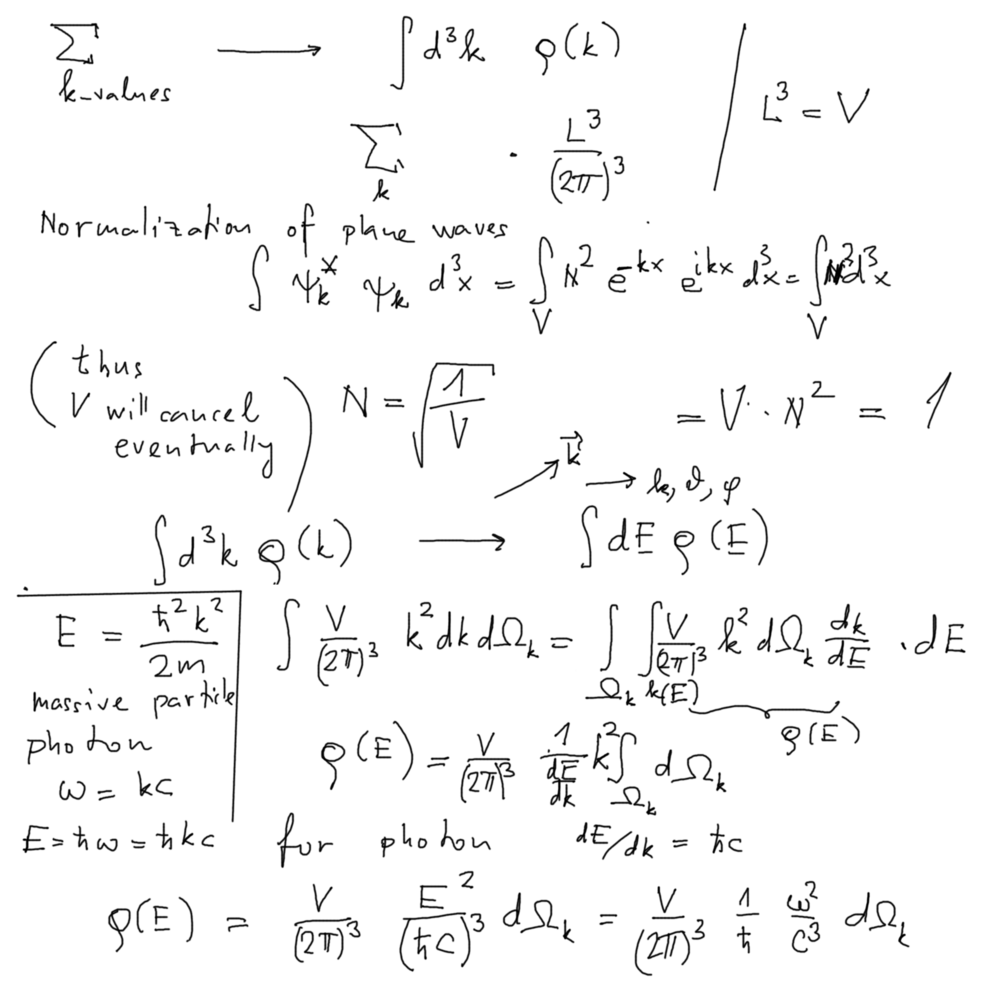
1120_Density_in_K-space_to-Energy.png
Eigenmodes of harmonic systems (coupled oscillations)
Formal transformation of the total energy
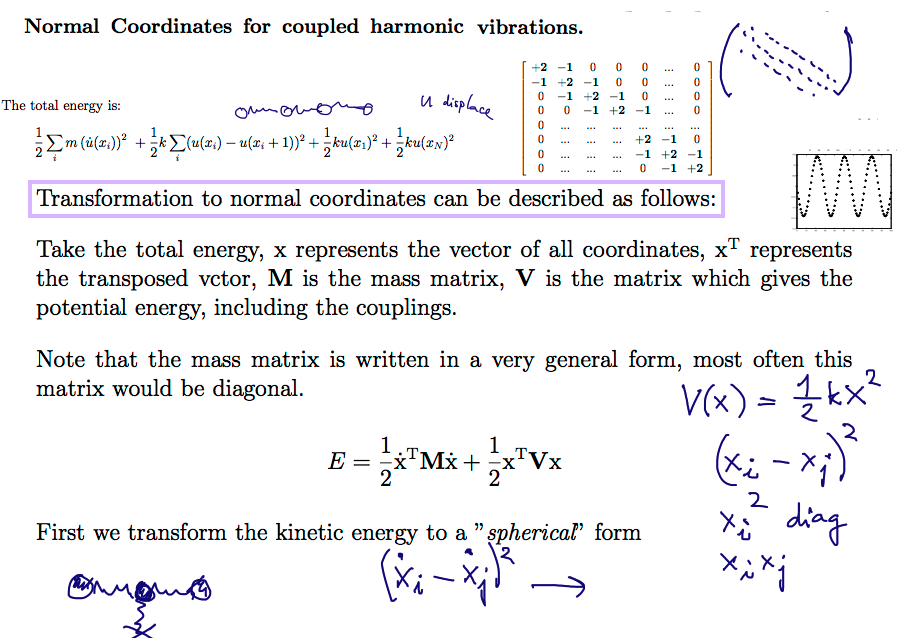
1140_Eigenmodes_Coupled_Harmonic_oscillations.png
Eigenmodes of harmonic systems (coupled oscillations)
Formal transformation of the total energy
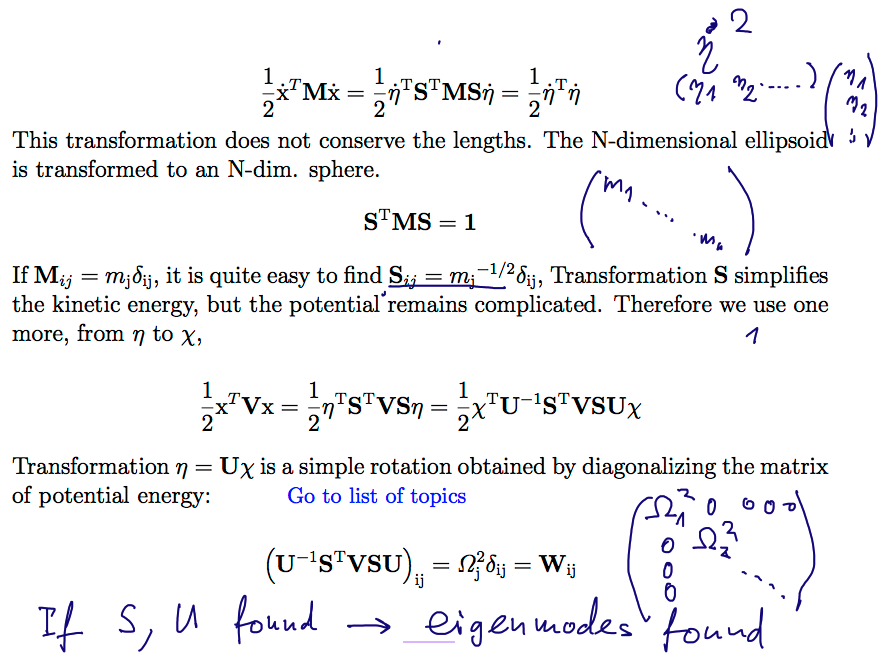
1150_Eigenmodes_via_transformations.png
Eigenmodes of harmonic systems (coupled oscillations)
Formal transformation of the total energy
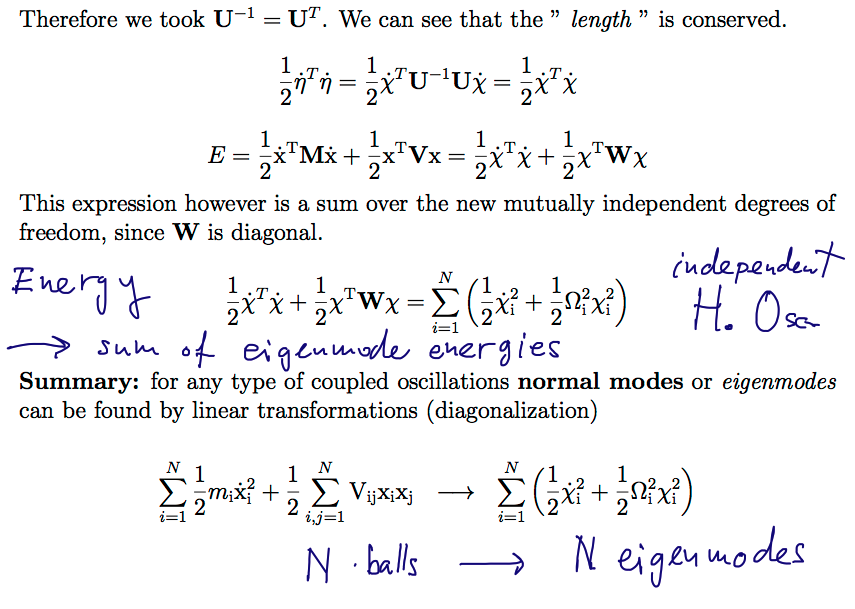
1160_Eigenmodes_via_transformations.png
Eigenmodes of harmonic systems (coupled oscillations)
Formal transformation of the total energy
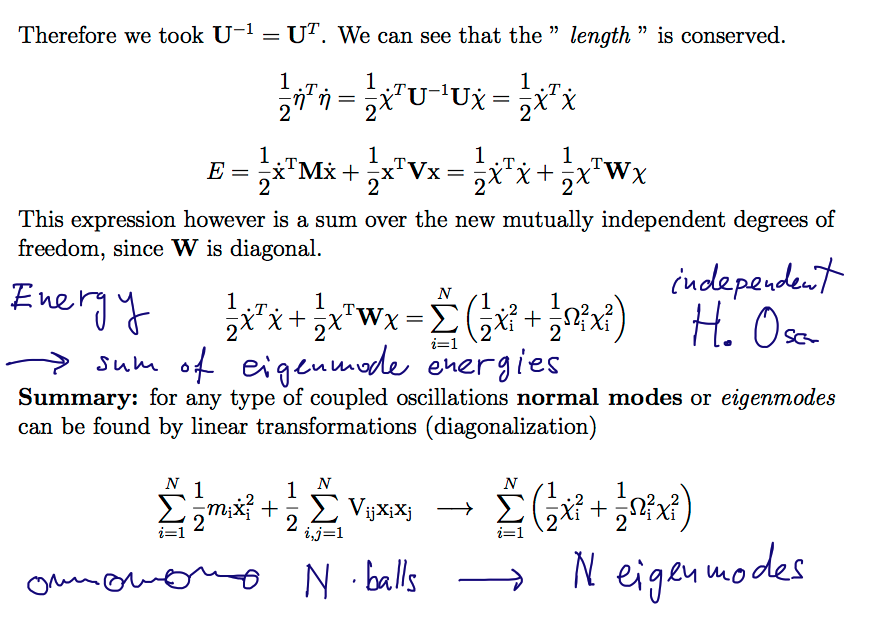
1170_Eigenmodes_via_transformations.png
Example: N balls connected by springs - coupled oscillations
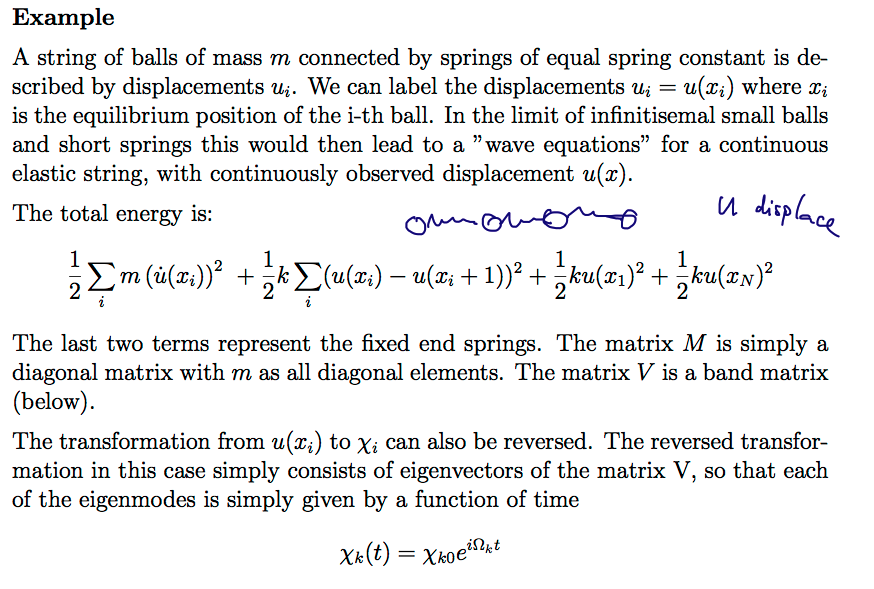
1180_Eigenmodes_N-balls-example.png
Example: N balls connected by springs - coupled oscillations
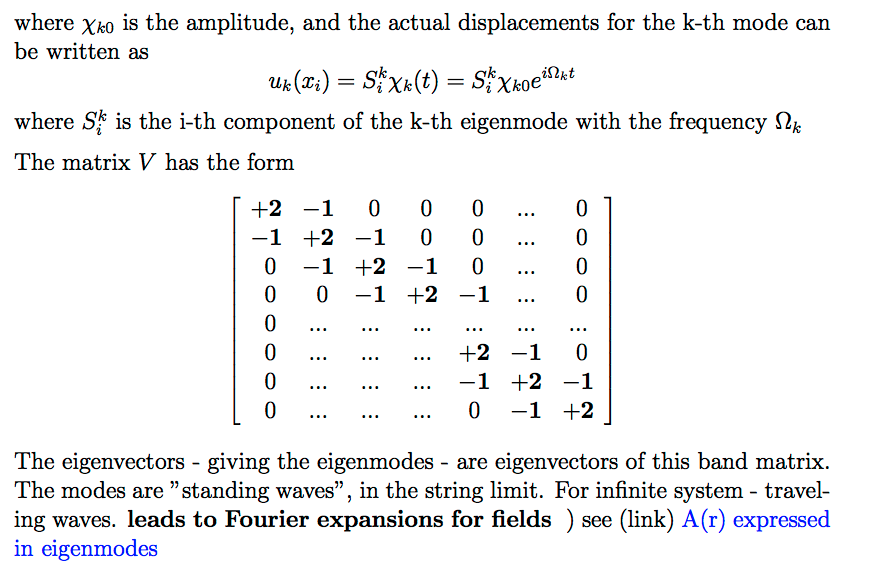
1190_Eigenmodes_N-balls-example_Matrix.png
Finding the eigenmodes - means expressing the system energy (hamiltonian)
as a system of independent harmonic oscillators
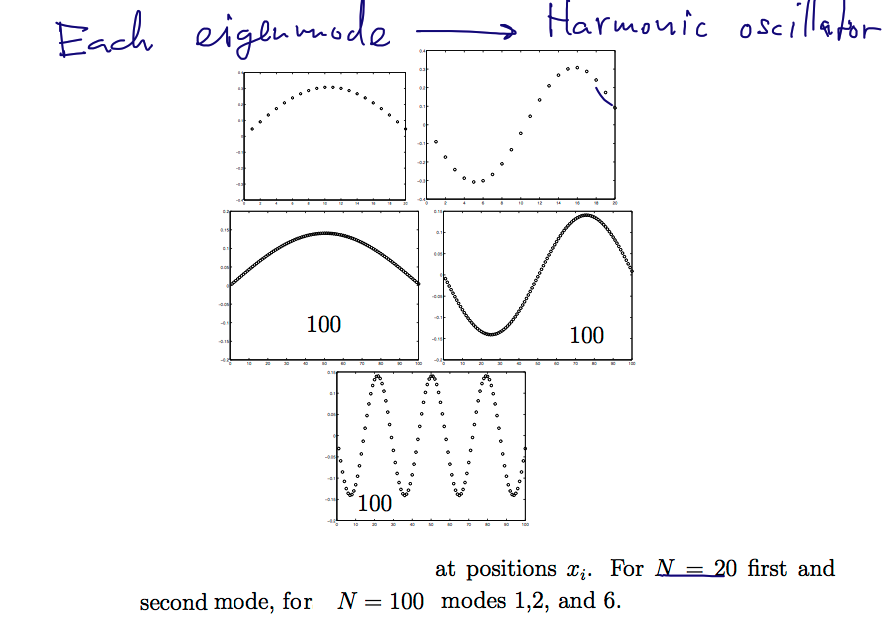
1195_Eigenmodes_N-balls-example_amplitudes.png
Finding the eigenmodes - means expressing the system energy (hamiltonian)
as a system of independent harmonic oscillators

1200_Eigenmodes_summary_Harmonic_oscillator.png
Algebraic method for the Harmonic oscillator - Creation and annihilation of "energy quanta"
The following three slides were just previewed; This will be detailed NEXT TIME
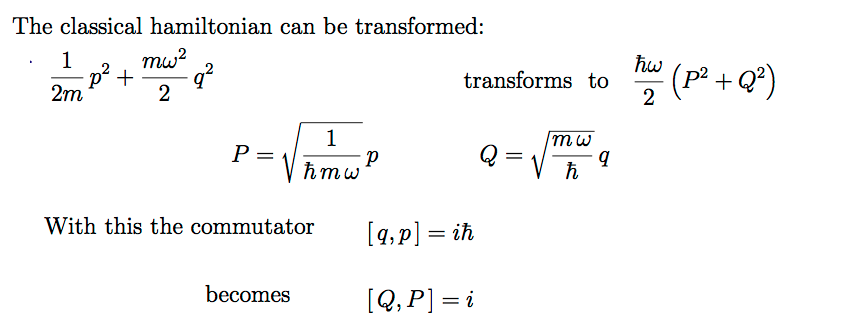
1220_Harmonic_Oscillator_Creation_Annihilation.png
Algebraic method for the Harmonic oscillator - Creation and annihilation of "energy quanta"
Here just previewed; This will be detailed NEXT TIME

1230_Harmonic_Oscillator_Creation_Annihilation.png
Algebraic method for the Harmonic oscillator - Creation and annihilation of "energy quanta"
Only previewed; This will be detailed NEXT TIME
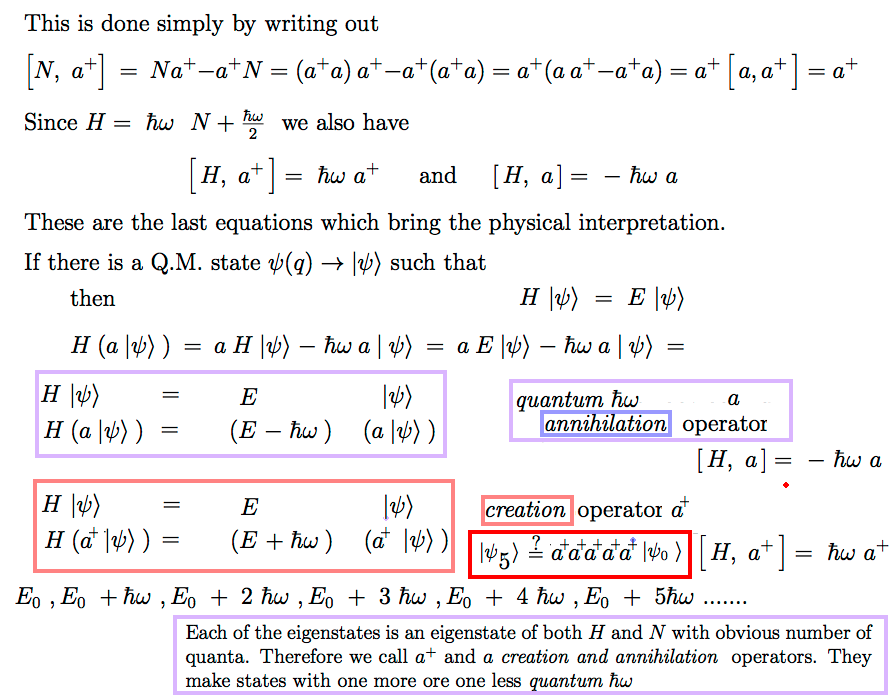
1250_Harmonic_Oscillator_Creation_Annihilation.png
Algebraic method for the Harmonic oscillator - Creation and annihilation of "energy quanta"
The last three slides will be detailed NEXT TIME