and
The Physics of Helium (starts below)
More facts about the physics of the simplest of the atoms - hydrogen - and hydrogen-like ions

0010.png
Hydrogen spectrum - an exercise - fill in the energies, L-values, N-values
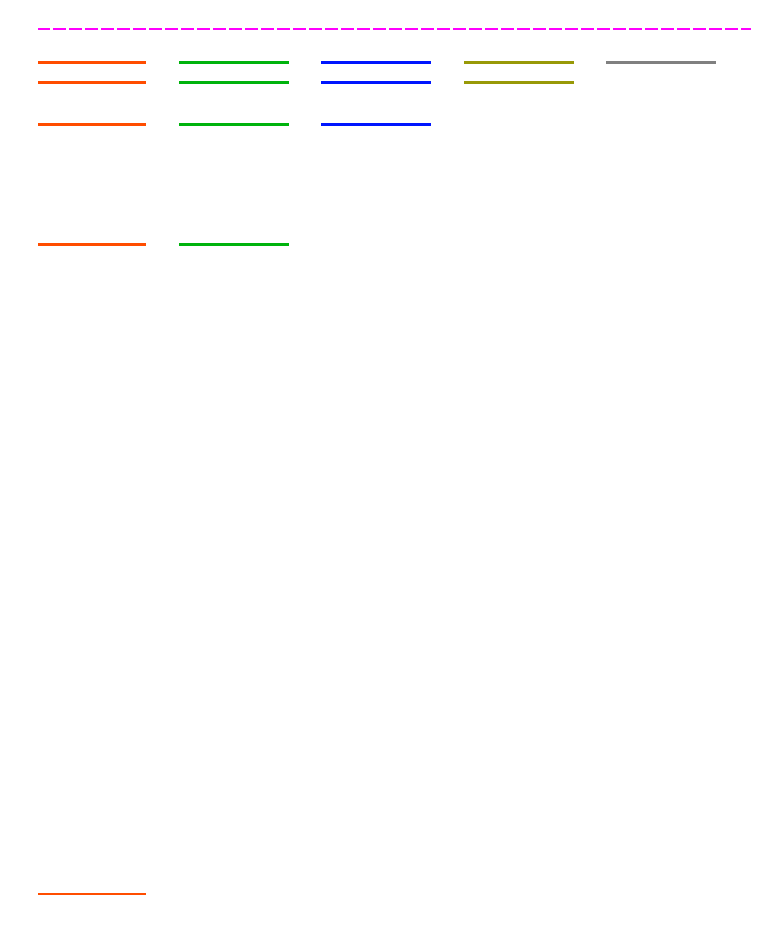
0013_hydrospec_larg.png
Hydrogen spectrum - an exercise - energies, L-values, N-values
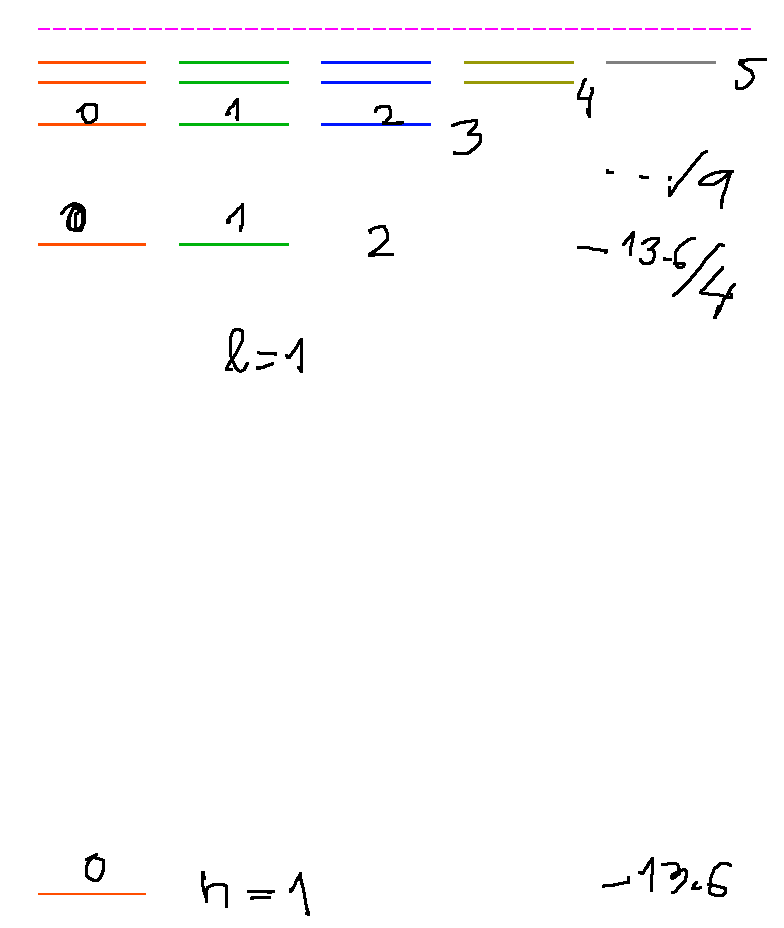
0015_hydrospec_larg-1.png
Hydrogen spectrum - an exercise - can be continued
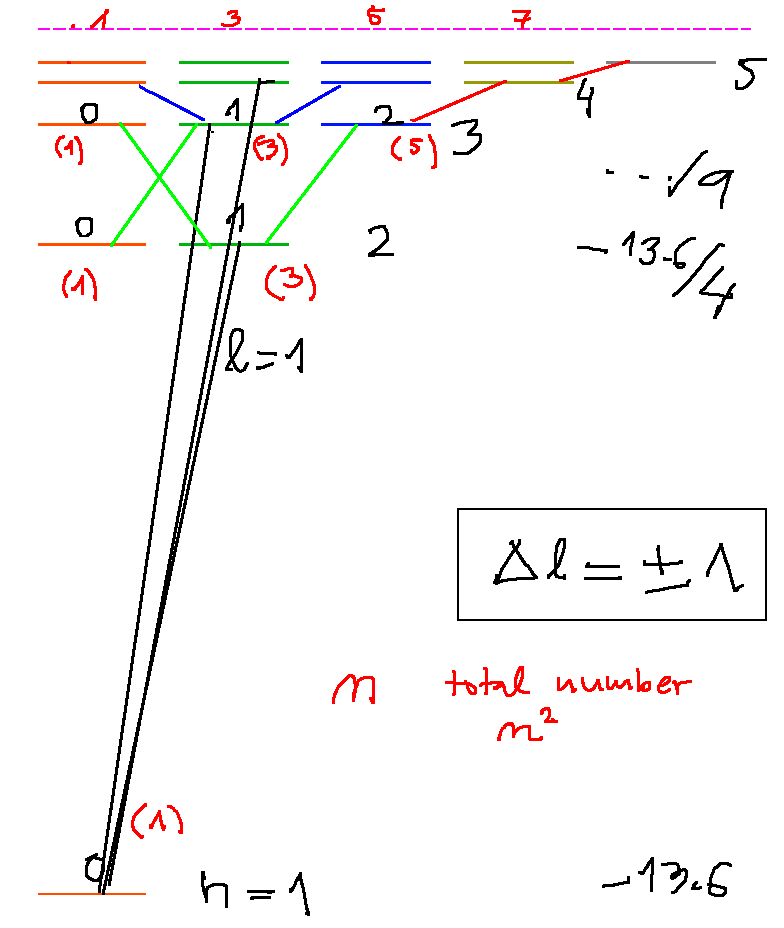
0017_hydrospec_larg-2.png
Radial functions of hydrogen (-like) atom (ion)

0020_Psi_hydrogen_citizendum.png
Spherical harmonics L=0 and L=1
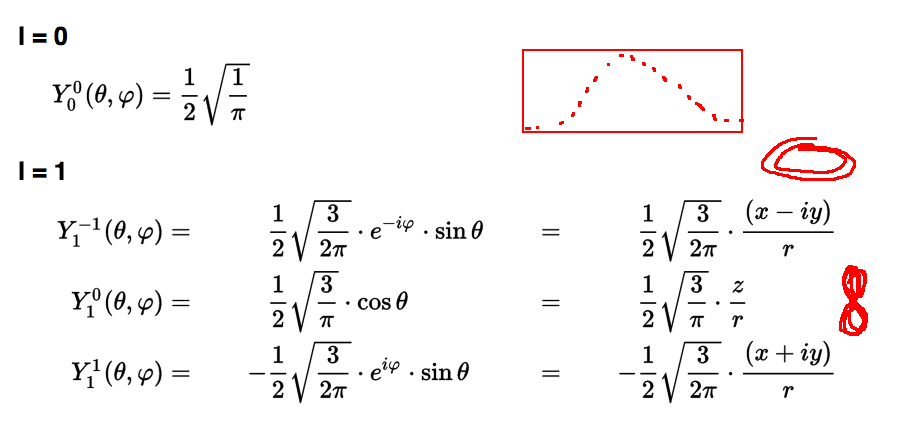
0025_Y_1_and_0_all_wiki1.png
Spherical harmonics L=2
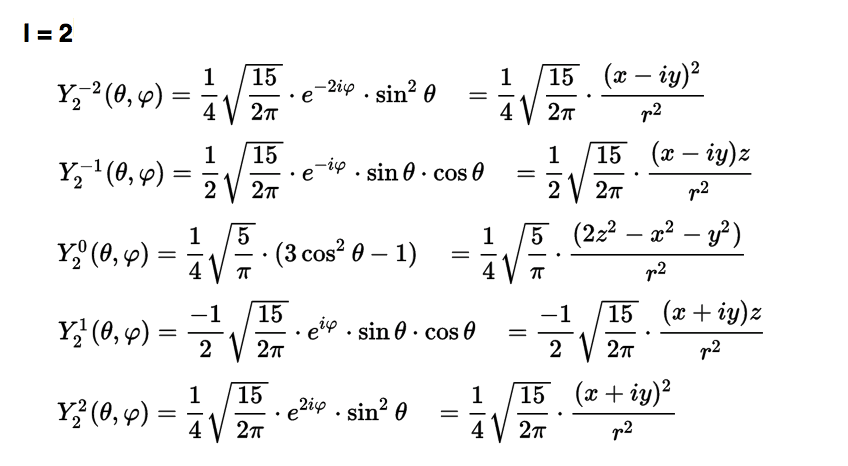
0029_Y_2_all_wiki.png
Spherical harmonics L=3
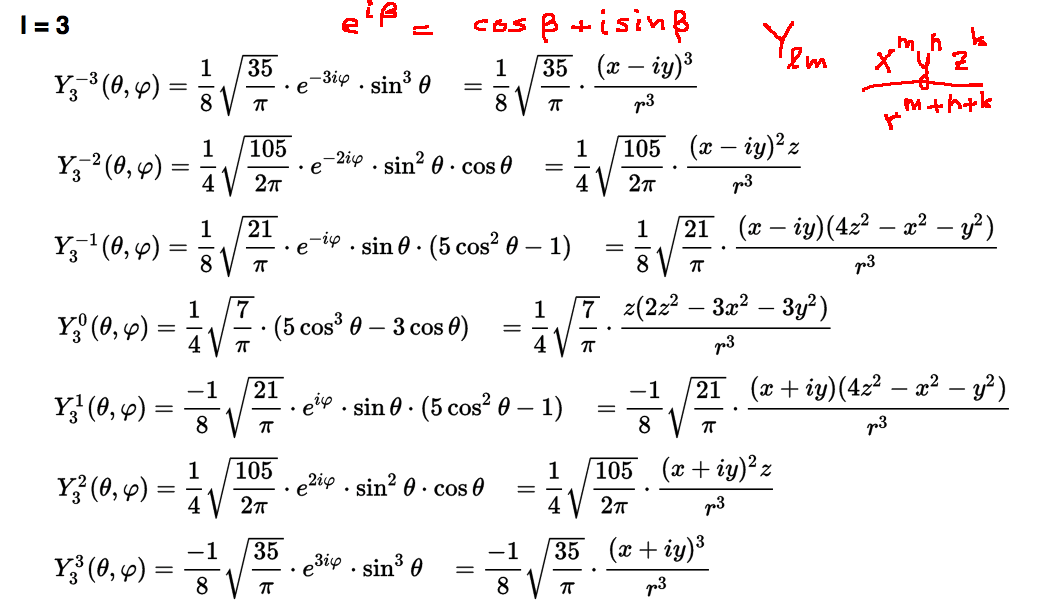
0033_Y_3_all_wiki-1.png
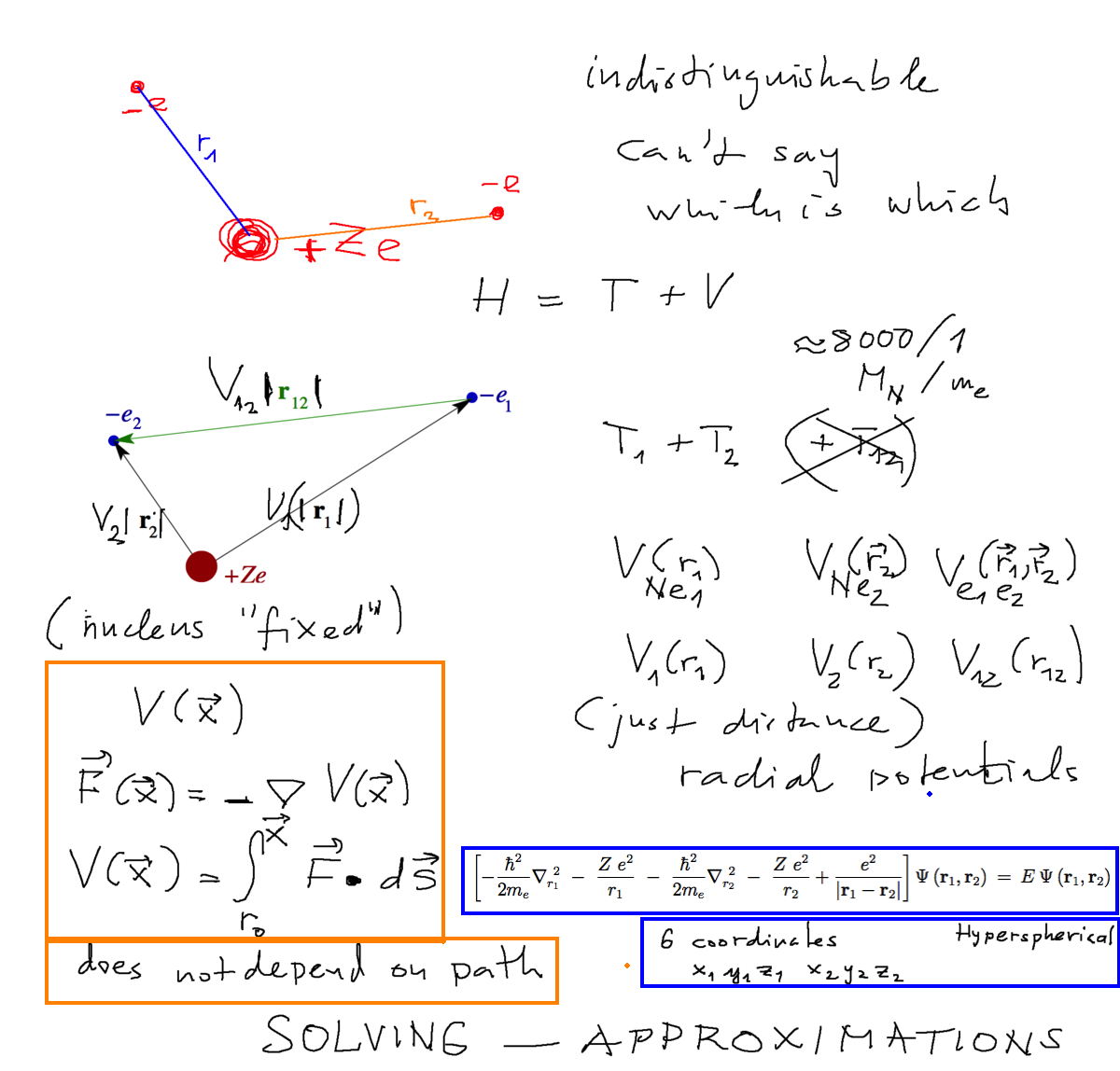
The model of helium atom Coordinate system - Hamiltonian
What is potential energy ( reminder on classical mechanics ) ( later on: electron indistinguishable = identical )
0050_Starting_Helium_Hamiltonian.png
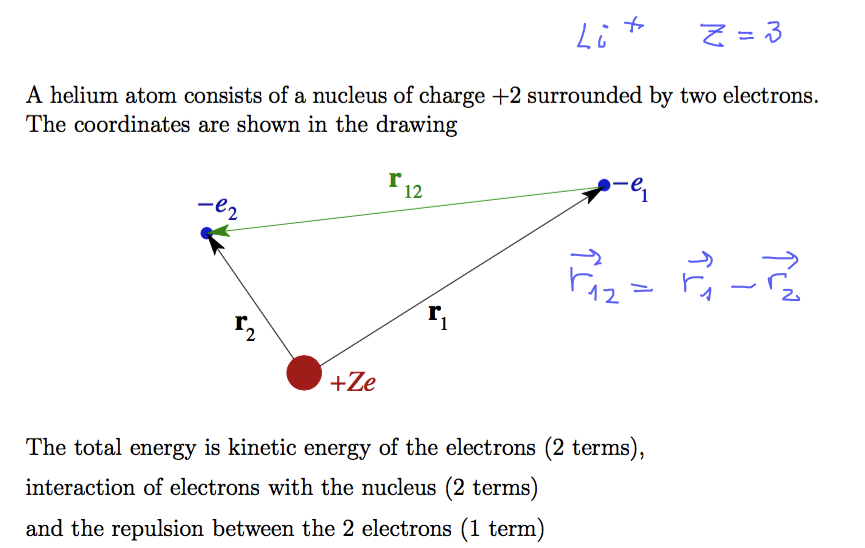
Helium atom - but also other ions with only 2 electrons remaining
singly ionized Li, doubly ionized Be, triply ionized B, and finally - 4 times ionized carbon .... etc up to U 90+
0055.png
Two spectra of helium atom - parahelium and orthohelium - energy scale "interrupted"
( some might have believed there are two types of Helium atom - no just two quite different states
these two states are the states of the spin - this is a very important feature )

0056_Para_Ortho_helium.png
Two spectra of helium atom - parahelium and orthohelium - energies correct
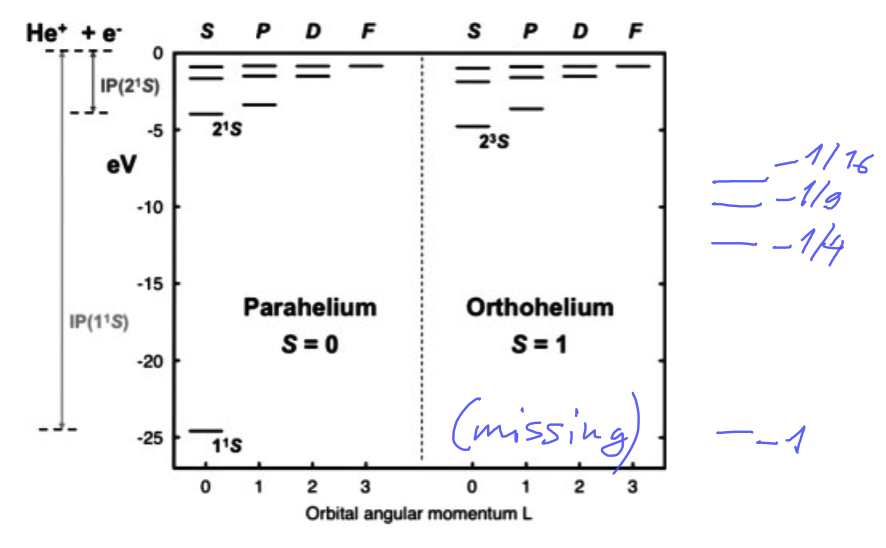
0057_Para_Ortho_helium_overview.png
( later on: electron indistinguishable = identical )
Symmetry requirement - eliminates "unnecessary parts of coordinate space (one possible perspactive)
Rotation of a "stick" with two "identical" ends - only half of the 360 degrees is the dynamical variable
for the whole circle (one end) 2 pi is the region - Q.M. continuity -> periodicity on 2 pi - allows only integer m in exp( i m phi)
for our stick - periodicity on pi ( not 2 pi ) - thus only even integer values m allowed in exp( i m phi)
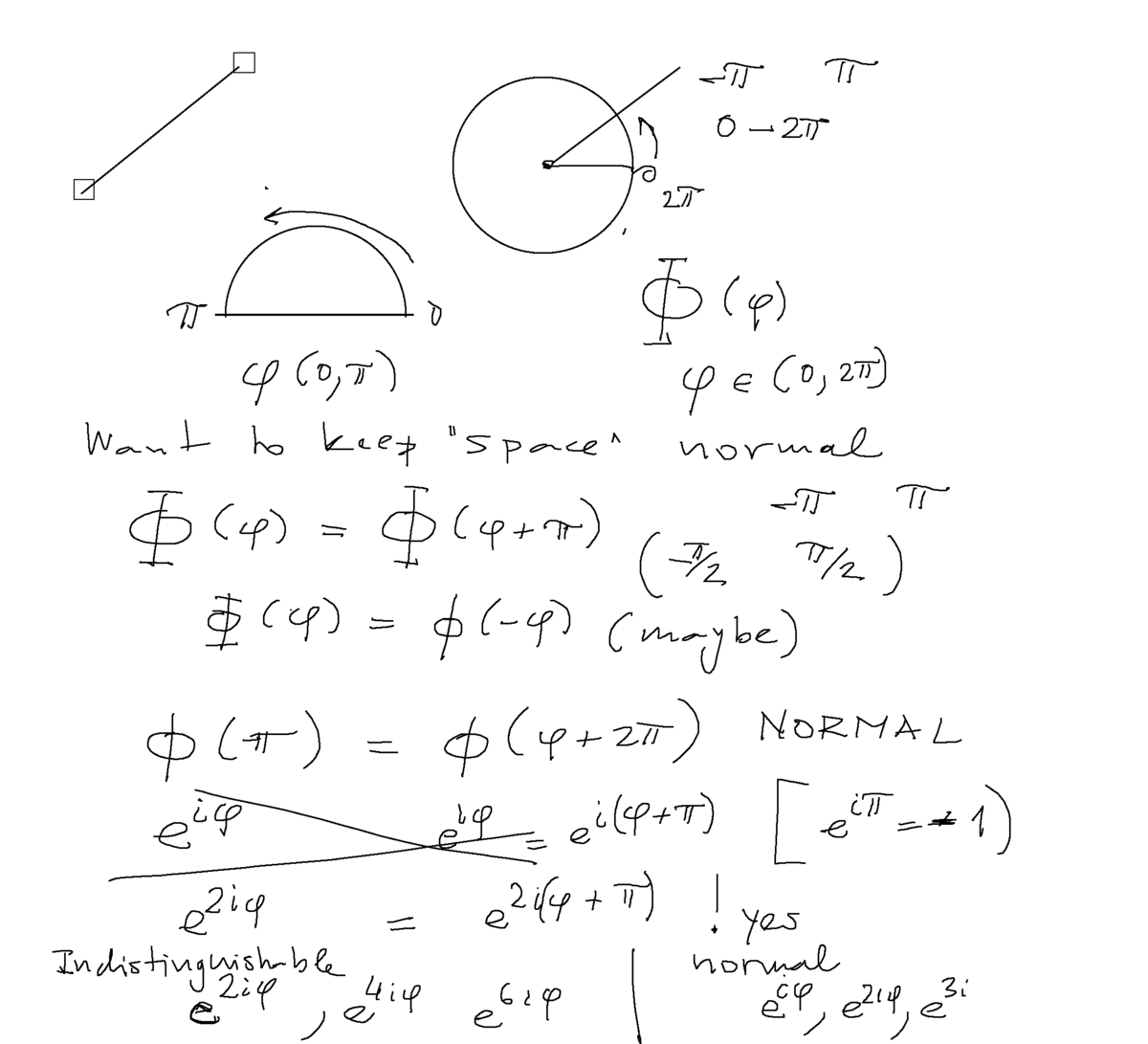
0060_Symmetry-eliminates_coordinate_spaces.png
Historically - Pauli principle first observation
Exchange symmetry used to put Pauli principle into a mathematical structure
- the necessary symmetry is - antisymmetry - minus sign by exchange - leads to ZERO function for the same "orbital"

0070_Pauli_Principle.png